Monday Pets
Lots of animals are well aware that bigger means scarier. In stressful or aggressive situations, for example, the hair or fur of chimpanzees, rats, cats, and even humans stands up on end (in humans, given our lack of fur, this results in goose bumps) in an effort to dissuade a potential attack. Elephant seals use a display called "rearing up" to make themselves look bigger - as if they need to look bigger in the first place!
Since some animals tend to be good at looking bigger than they truly are, visual cues may not actually be a reliable method of sizing up another individual. In addition…
Most dog owners think that their dogs can tell what they're thinking. Or at least, in some sense, they will insist that their pet pooches can sense their emotions, and respond accordingly.
Indeed, a man by the name of Karl Krall (say that three times fast) thought that there exist some sort of psychic connections between man and animal. And he thought he could prove it.
In this telepathy experiment between human and dog Karl Krall (on the right) tried to detect the thinking radiation he assumed to flow between the two. Krall was a rich dealer in diamonds who had founded his very own…
Whether you're a dog, a cat, or a grad student who hasn't been home to shower for a few days, fleas are a major problem. They make skin itch. And NOTHING is worse than itchy skin.
But...
Do you know WHERE the fleas are? Where they like to hang out and guard their little flea eggs? Where's the best place for a flea to get a decent night's sleep, or a delicious snack? These are important questions. Lucky for us, Hsu, Hsu, and Wu of the Department of Entomology at National Taiwan University have the answers. And this paper, dear readers, is pure blogging GOLD.
Now, if you wanted to find out…
Your humble narrator finds himself sick with a cold, so here's a post from the archives.
There is considerable research on how children interact with other children and with adults, and how child development can be influenced by those interactions. But research on children's interactions with non-human animals seem to be limited. Given how ubiquitous pets are in the homes of children (at least, in WEIRD cultures), it is somewhat surprising that there hasn't been more work on the way pet ownership might affect child development.
According to the US Humane Society:
There are approximately 77…
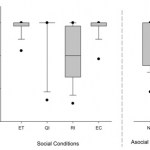
Cooperation and conflict are both a part of human society. While a good deal of the academic literature addresses the evolutionary origins of conflict, in recent years there has been an increased focus on the investigation of the evolutionary origins of cooperative behavior. One component of cooperative behavior that might be present in other animals is aversion to inequity. Some scientists have suggested that inequity aversion may itself be the main factor driving the enforcement of cooperation. Put simply, inequity aversion is the resistance among partners to unequal rewards following…
At least one dog can be found in forty percent of US households, and forty percent of those owners allow their dogs to sleep on their beds. To put this in perspective, in a family with five children, two of them can be expected to become dog owners, and one of them will probably allow the dog to sleep on his or her bed. In an undergraduate lecture class of two hundred, eighty of those students come from homes with at least one pet dog. So as you might expect, dogs are a big business! In 2007, the pet industry was worth about $40 billion in the US, with dogs responsible for the largest share…
For today's dose of monday pet blogging, head on over to a piece that I wrote for Scientific American that went up today. I used the invitation as an opportunity to a dig a little deeper into the story of Belyaev and his domesticated silver foxes (I previously wrote about them, here and here)
Dogs are pretty smart. They can have huge vocabularies, they can infer meaning in the growls of other dogs, and they can effortlessly figure out if other dogs want to play or fight with them. But their intelligence might be limited to the social domain; indeed, while they outperform chimpanzees in social tasks, chimpanzees outperform them in many other tasks. And they might have developed their impressive social skills as merely an accident of natural and artificial selection.
Previous research has shown that dogs can use lots of different forms of human communicative signals to find food,…
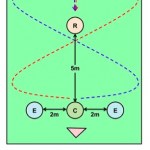
Predator-prey interactions are often viewed as evolutionary arms races; while predators improve their hunting behaviors and their ability to sneak up on their prey, the prey improve upon their abilities to detect and escape from their predators. The problem, of course, is that there is a trade-off between maintaining vigilance - the attention necessary to be consistently aware of others in the environment takes quite a bit of physical and mental energy - and doing all the other things that an animal must do, such as finding its own food. As a result of this trade-off, many social species,…
I will be reposting some dog-related posts from the archives in the coming few weeks as I prepare for the course I'm teaching this semester on dog cognition. Please let me know if you find something inaccurate or unclear.
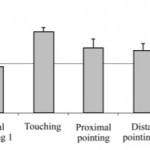
Domesticated dogs seem to have an uncanny ability to understand human communicative gestures (see here). If you point to something the dog zeroes in on the object or location you're pointing to (whether it's a toy, or food, or to get his in-need-of-a-bath butt off your damn bed and back onto his damn bed). Put another way, if your attention is on something, or if your…
Different dog growls mean different things, right? Probably. But can you tell the difference?
Here's a dog growling when someone is trying to steal its food: link to mp3.
Here's a dog growling at a stranger: link to mp3.
You probably can't tell the difference. Neither could I. Dogs can. Surprised? Probably not. But, this is the first experimental evidence that dogs use different communicative vocalizations during social encounters with other dogs and with humans, depending on the situation.
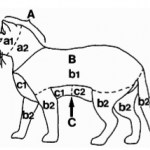
The researchers recorded dog growls in three contexts: food guarding from another unfamiliar dog (…
"But wait," you say. "Anteaters aren't pets!" Well, I didn't think so either. But Salvador Dali had a pet anteater. And that's good enough for me.
Figure 1: Salvador Dali taking his pet anteater for a stroll. (Source)
The Giant Anteater, Myrmecophaga tridactyla, only eats ants and termites, making it a myrmecophage. (Hey, Alex Wild, now I get what Myrmecos means!) In 1984, a researcher named Kent Redford was interested in the foraging behaviors of the giant anteater, and the relationship between these anteaters and their prey, colonies of highly social insects. So Redford went to Brazil to…
In general, the ability to attribute attention to others seems important: it allows an animal to notice the presence of other individuals (whether conspecifics, prey, or predators) as well as important locations or events by following the body orientation or eyegaze of others. We've spent a lot of time here at The Thoughtful Animal thinking about how domestication has allowed dogs to occupy a unique niche in the social lives of humans. They readily understand human communication cues such as eye-gaze and finger-pointing, and capitalize on the infant-caregiver attachment system to have their…
From the archives...
Figure 1: Does Mickey feel empathy?
It probably depends on how you define empathy. Empathy, by any definition, implies emotional sensitivity to the affective state of another. Sometimes the empathy response is automatic or reflexive, like when babies start to cry upon hearing another baby crying. Sometimes a strong cognitive component is required, such as for compassion. A more specific understanding of empathy requires similarity between the affective states of the observer and the observed, with an understanding that the observer feels a certain way because he has…
I am quite full from the last minute Fourth of July dinner that my brother and I threw together - featuring grilled chicken-apple sausages, roasted pork tenderloin with lemon-pepper dry rub, and chocolate peanut butter cookies. Too full to blog. Instead as I'm working my way through season six of Buffy on Netflix, I've got something different for you today.
Instead of the usual Monday fare, I want you all to go over and say hello to The Dog Zombie.
She describes herself thusly:
The Dog Zombie studies dog brains by pursuing DVM and MS degrees. She is currently in her research year, between…
She: "What are you writing about?"
Me: "Cognition in cold-blooded animals."
She: "Hot."
Most people who study cognition focus on mammals or birds. But I hope I've convinced you that other animals are important to investigate as well. One research group at the University of Vienna likes cold-blooded critters. Turtles and lizards and such. They argue:
Reptiles, birds and mammals have all evolved from a common amniotic ancestor, and as such they are likely to share both behavioural and morphological traits. However, this common ancestor lived around 280 million years ago and so it is equally…
Happy Father's Day, everyone!
I spent a lot of time today thinking back to why I started blogging in the first place, while I was at my parents house doing the other-than-science things that I love to do: playing with the dog, cooking, gardening. I realized that I've not done enough of that stuff lately.
I've only been seriously doing the blog thing (in the current format) since January, and I've now been here at Scienceblogs around two months, so it was time to reflect. The transition from Wordpress obscurity to Scienceblogs prominence happened relatively quickly for me, and I think it's a…
I've decided I want to cover some recent research on social cognition in domesticated dogs. But first, we need some background. So here's a repost from the old blog.
Today I want to tell you about one of my most favorite studies, ever, of animals. Are you ready? It's a FIFTY YEAR LONG longitudinal study of captive silver foxes in Russia. Gather around, pour yourself a cup of your favorite beverage, get comfortable, and enjoy storytime.
In 1948, Soviet scientist Dmitri Belyaev lost his job at the Department of Fur Animal Breeding at the Central Research Laboratory of Fur Breeding in Moscow…
Zen recently wrote mentioned this study on his blog, so I thought it was time to dredge it out of the archives. Also, I've just returned from APS (see my daily recaps here here and here), and I am TIRED.
Domestic animals and their wild counterparts can be different in big ways; there can be differences in morphology (physical characteristics), physiology, and behavior. These changes may depend on spontaneous adaptations to captivity or to artificial selection pressures arising from the motivation for domesticating the animal in the first place.
One change that is often observed as a result of…
Lately, a paper to be published in the June edition of the American Naturalist has been getting some attention. The findings that are getting reported out of this paper didn't make sense to me, but I wondered if this was an issue with accuracy in reporting. So I went and found the paper. Turns out that the reporting is accurate, its the actual findings from the paper that confuse me. I really wanted to make sense of this paper, so I've been waiting a while to blog about it. But I can't make sense of one key finding.
Figure 1: An artist's rendition of me, being confused. If, you know, I were…