"A few centuries ago, the pioneer navigators learnt the size and shape of our Earth, and the layout of the continents. We are now just learning the dimensions and ingredients of our entire cosmos, and can at last make some sense of our cosmic habitat." -Martin Rees
You might think that Jupiter is the largest planet in the Solar System because it’s the most massive, but that’s not quite right. If you kept adding mass to Saturn, it would get larger in size, but if you kept adding mass to Jupiter, it would shrink! For a given set of elements that your planet is made out of, there’s a maximum size it can reach, that’s somewhere in between the mass of Saturn and Jupiter in general.
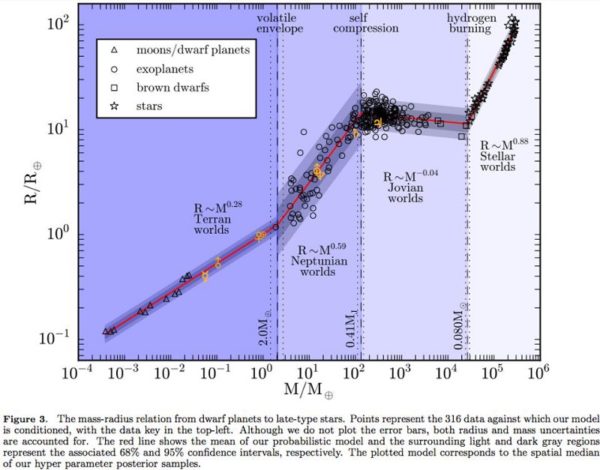 Planetary size peaks at a mass between that of Saturn and Jupiter, with heavier and heavier worlds getting smaller until true nuclear fusion ignites and a star is born. Image credit: Chen and Kipping, 2016, via https://arxiv.org/pdf/1603.08614v2.pdf.
Planetary size peaks at a mass between that of Saturn and Jupiter, with heavier and heavier worlds getting smaller until true nuclear fusion ignites and a star is born. Image credit: Chen and Kipping, 2016, via https://arxiv.org/pdf/1603.08614v2.pdf.
Our Solar System is on the dense side of things, meaning that we’ve discovered a large number of exoplanets out there that are approximately twice the physical size of Jupiter without becoming brown dwarfs or hydrogen-fusing stars. For worlds like WASP-17b, where we’ve measured both the radius and mass, we find that they’re only about half the mass of Jupiter, despite being double the size.

Interesting info on the mass vs. size thing; I had naively thought they would reasonable correlate for all gas giants, but I guess not.
Amusing factoid: every planet in our solar system is more massive than all the planets smaller than it, combined. Thus, Venus has more mass than Mercury+Mars, Earth has more mass than Mercury+Mars+Venus, Uranus has more mass than Mercury+Mars+Venus+Earth, and so on.
Information on the different planet is describe in EARTHMEASURED