Biological networks
Metastatic melanoma tumors. Left exhibits low or absent expression of RASA2 and reduced survival, typical of about 35% of patients. The sample on the right exhibits high RASA2 expression and increased survival
Rates of melanoma are increasing, even as the rates of other common cancers are decreasing. According to the Melanoma Research Alliance, it is the most common cancer diagnosis in young adults 25-29 years old in the United States, the second most common cancer in young people 15-29, and its incidence has tripled in the last 30 years.
What are we doing about it? The Weizmann Institute’…
One day in the future, we may be treating our ailments with microbiotic combinations designed specifically to correct imbalances in our personal microbiomes. We’ll bring our prescriptions on rewritable paper and pay using shimmery optical chips embedded in our cell phone cases or maybe our jewelry. Or we’ll be waiting in our doctor’s office for a simple test of our microbiogenome to see if a light-based nanoparticle delivery treatment is working, while watching iridescent optical displays that change as we move...
These future scenarios (and many more) are all imaginary, but…
“Inclusion bodies – those clumps of protein that are found in the brain cells of Alzheimer’s patients – are, sadly, a product of aging,” says Dr. Maya Schuldiner. “They can form naturally in practically all cells, but when these cells get old, the mechanism for clearing them away starts to fail.”
That is not great news for those of us who are already seeing signs of incipient dementia every time we forget a name or misplace our keys. But of course there is good news too. Schuldiner has discovered a “detergent” that cells make to wash away those nasty protein clumps. And she believes that, in…
Here is today's scientific image:
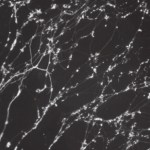
This delicate, fluffy object is a cytoskeleton viewed under a fluorescence confocal microscope. Below is a time-lape video of the process. For an explanation of why the cell's actin fibers twist around into this shape, go to our website.
[embed]https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iLm0Ojngjc4[/embed]
Indeed, all three of today's new articles involve crucial cellular dynamics: cutting up unfolded proteins with pared-down molecular "scissors" and binding to metal ions in proteins. In other words, within that lovely shell-like cytoskeleton, the cell is quite a busy…
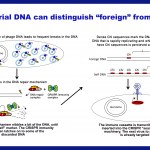
Foreigner or native-born? Your immune system discriminates between them, as do those of bacteria. Yes indeed, bacteria do have immune systems – pretty complex ones at that. And like any useful immune system, the bacterial ones must have a good technique for distinguishing “foreign” from “self.”
You may even have heard of the bacterial immune system: It’s called CRISPR, and it’s used in biology research around the world for DNA engineering and genome editing. CRISPR normally inserts short DNA sequences taken from phages – viruses that invade bacteria – into special slots called spacers within…
To all bits of clockwork that are adjusted in our bodies according to our day-night timetable, we can now add two more: cancer growth and the schedules of our internal complements of bacteria.
Cancer, according to a new Weizmann Institute study, may grow and spread more at night. In this scenario, our cells are getting messages left and right, day and night, and taking them in through the specialized receptors on their outer membranes. During the daytime, our bodies produce natural “wake-up” hormones, and these apparently, take precedence over other incoming messages, their receptors…
At the level of biomolecules, life boils down to two basic principles: sequence and folding. We know, for example, that the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA contains our genetic blueprint, but the way that our DNA is folded and wrapped up in each chromosome helps determine which genes are easily accessible for copying. Proteins – sequences of amino acids – fold into intricate shapes before assuming their duties. So it is no surprise that the third main molecular sequence in the cell – the RNA, made up of single strands of nucleotides – folds as well. Nucleotides are built to pair up – DNA…
Science on Tap, which happened in Tel Aviv last Weds. eve, was as great a success as ever. Ariela Saba, one of our Weizmann writers, attended one of the talks. Here is her report:
Right around now – in some 55 bars all around Tel Aviv and Jaffa – Weizmann Institute scientists are starting their talks. Some of the patrons are in the middle of dinner; others are already sipping after-dinner drinks. Here in The Container at the Jaffa port, Dr. Eran Elinav is just warming up. From where I am sitting, I can see into the kitchen: Plates are making their way out laden with fluffy white bread, butter…
What effect does a constant stream of engaging stimuli have on our relationships? On our social structure as a whole? What percentage of our actions is influenced by others, and how does this translate, at some point, into group behavior?
Neurobiologists Prof. Alon Chen and Dr. Elad Schneidman of the Weizmann Institute and their team members have been using mice to investigate these questions. Chen and Schneidman approach the group as a network composed of the joint behavior patterns of mice that had had their fur dyed in bright, glow-in-the-dark colors. Among other things, this enables the…
Since the haiku post was well received, and since we have another three pieces online today – each on a different finding and each interesting in its own right – I have decided to return to the haiku format. Among other things, there is something quite satisfying about distilling complex scientific findings down to 17 little syllables – like writing the perfect tweet, but more so.
In any case, follow the links to read more:
A burst of enzymes:
A transcription traffic jam
Watch for gene speed bumps
Genetics can rid
The poison from potatoes
Or add it elsewhere
image: Thinkstock…
To attain knowledge, add things every day. To attain wisdom, remove things every day.
Lao Tsu
Apparently our nervous systems develop according to the Chinese philosopher’s principle of being and not being. As our nerve cells grow, they send out long extensions – axons – throughout the developing tissues. And as they reach out, some are also pruned back. The configuration of nerve endings we finally possess depends on both what was added and what was removed.
Which axons will complete their developmental journeys and which will be pruned back? For some, it is simply a matter of fate.
But in…
Poetry is finding its way into our consciousness at the Weizmann Institute: At the recent, fourth annual Science on Tap evening, which the Institute hosts in Tel Aviv, several poets joined in the fun, reading from their work before and after the talks given by scientists in over 60 filled-to-capacity pubs and cafes around the city. And calls have gone out for entries to the Ofer Lider creative writing contest – open to scientists (writing in Hebrew). The contest is named for Prof. Ofer Lider, an Institute scientist who, sadly, died young and who wrote poetry because he believed that…
Does your face reveal what’s in your heart? It might – even more than you know. Take, for instance, a common group of birth defects – forms of a disorder called DiGeorge syndrome. Around one in 4000 is born with this syndrome, which arises from a deletion of a short segment of chromosome 22. Among other problems, this deletion nearly always involves deformations in both the face and the heart.
Sculpture: Igor Mitoraj
The Institute’s Prof. Eldad Tzahor had already shown that face and heart go together: Very early on in the developing embryo, the progenitor cells that will…
One of our scientists, Dr. Assaf Vardi, is off on a month-long cruise. He is on the Knorr, a research vessel operated by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institute, with a team from the Weizmann Institute and another four research teams on a route that will take them from the Azores to Iceland. On the way, they will be sampling the plankton; among other things they want to understand how the molecular processes that take place in these single-celled organisms affect everything from the ocean's food chain to the oxygen in the atmosphere. Rose Eveleth is posting from the ship daily on the…
This week's new Weizmann science stories are on ants and bats. Two different models for investigating human behavior? Yes, but not exactly in the ways you might imagine, and so much more than that.
Dr. Ofer Feinerman, the "ant scientist," is a new member of the Physics Faculty. In his graduate research under Prof. Elisha Moses in the Physics of Complex Systems Department, Feinerman created artificial circuits out of neurons. Now he has turned to investigating the complexities of ant societies. What, you might ask, do neurons and ant colonies have to do with physics? The answer is: They…
What does a tiny patch of salamander retina see when it watches a movie? Weizmann Institute scientists, together with Dr. Ronen Segev at Ben-Gurion University, performed this experiment - literally showing film sequences to snippets of live retina tissue and recording the interactions between their 100 or so active neurons.
Seeing, as we know, is 3/4 interpretation and, contrary to common belief, this interpretation begins in the eye, before an image ever reaches the brain. Dr. Elad Schneidman and his colleagues found that unique patterns of neuron activity could be identified: There were…