California drought
My friend Peter Gleick tosses this question aside and informs us that there are actually better questions. Is California having a wet year? How does the snowpack look? Are the reservoirs filling up? Will the groundwater recharge? Will the forests in the Sierra recover with all this precip? Will farmers get all the water they want this year? Will a wet year help the endangered salmon? Will governor Brown cancel the drought declaration? Can Californians stop conserving water and throw some on their lawn?
It turns out that the answer to most of these questions is not what you would assume…
Populations around the world face many severe water challenges, from scarcity to contamination, from political or violent conflict to economic disruption. As populations and economies grow, peak water pressures on existing renewable water resources also tend to grow up to the point that natural scarcity begins to constrain the options of water planners and managers. At this point, the effects of natural fluctuations in water availability in the form of extreme weather events become even more potentially disruptive than normal. In particular, droughts begin to bite deeply into human well-being…
The latest episode of Ikonokast, the science podcast Mike Haubrich and I do, is now up. This is an interview with Pacific Institute's Peter Gleick. We talk about the California drought (past, present, and future), Syria, virtual water, El Nino and climate science denialism.
You can hear the podcast here: WHAT ABOUT WATER? DR. PETER GLEICK OF THE PACIFIC INSTITUTE.
California voters feel increasingly squeezed by their drought, according to a new USC Donrslife/Los Angeles Times poll.
September 11, 2015 — As one of California’s most severe droughts on record continues to worsen, more than one in three state voters say the drought has had a major impact on them and the lives of their families, according to results from the latest USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences/Los Angeles Times Poll.
Thirty-five percent of California voters said the drought has had a major impact, 50 percent said it has had a minor impact, and 14 percent said it has…
Heather Cooley and Peter Gleick
California is in a severe drought – four years long now. But what does the drought really mean for the things we care about: food production, fisheries, industrial activities, rural communities? As part of the work of the Pacific Institute to evaluate both the impacts of water problems and identify smart solutions, we’ve just released the first comprehensive assessment of the actual impacts of the drought for California agriculture.
Many commentators and analysts have worried especially about California’s agricultural sector, which is a major water user and has…
Human released greenhouse gas pollution changes the climatic system through a variety of mechanisms. Trade winds and jet streams change their patterns of movement, and the distribution of moisture in the air changes, with precipitation either lacking more than usual or being more abundant than usual. The patterns of movement of major air masses and the increased bifurcation of air masses into more wet than usual and more dry than usual can result in long periods where region experiences excess precipitation or a lack of precipitation. When the latter happens, there can be a drought.…
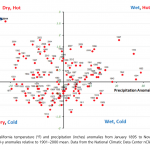
A paper just out now in PNAS by Noah Diffenbaugh, Daniel Swain, and Danielle Touma shows that "Anthropogenic warming has increased drought risk in California." From the abstract:
... We find that although there has not been a substantial change in the probability of either negative or moderately negative precipitation anomalies in recent decades, the occurrence of drought years has been greater in the past two decades than in the preceding century. In addition, the probability that precipitation deficits co-occur with warm conditions and the probability that precipitation deficits produce…
California’s hottest and driest drought in recorded history has shifted the sources of electricity with adverse economic and environmental consequences. The Pacific Institute has just completed and released a report that evaluates how diminished river flows have resulted in less hydroelectricity, more expensive electricity from the combustion of natural gas, and increased production of greenhouse gas emissions.
The current severe drought has many negative consequences. One of them that receives little attention is how the drought has fundamentally changed the way our electricity is produced.…
The California drought continues.
While we do not know yet what the rest of the wet season will bring – and while we hope for the major storms needed to recharge our rivers, groundwater and reservoirs – it seems increasingly likely that California will not see enough precipitation to get out of the very deep deficit that three years of drought (so far) have produced.
There is, however, some misleading and confusing information out there. Some are already arguing that California’s rainfall is nearly back to normal or that because there may have been more serious droughts in the past we needn’t…
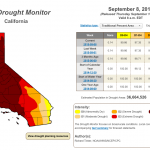
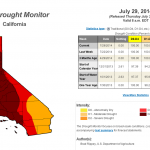
The US Drought Monitor produces an assessment of drought conditions every week. The drought in California has taken a large jump over the last few days, with the highest category, "Exceptional," jumping from 36.49% to 58.41%. At the start of the calendar year, that category was represented in California by 0%, so this is a continuation of an ongoing trend. The image above is the current map from US Drought Monitor.
I made a couple of other graphics that demonstrate the problem.
This is the percent area in California covered by severe to exceptional drought since the most recent time that…
Possibly both.
Climate change certainly has a huge effect. Increased evaporation, decreased snowpack, the stalling of air masses that cause more drying and less wetting, which in turn is caused by changes in the jet stream, which in turn is caused by "Arctic Amplification," an effect of global warming, are major causes of a three year drought coming hard on the heels of a decade of near-drought dry.
But also, Californian approaches to water management have been an issue. I recently learned that there are communities in California that don't even have water meters on people's houses. What…
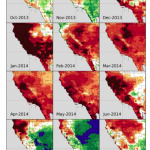
The end of the rainy season in California is arriving in a few weeks, and the April 1st snowpack measurement, which is a key indicator of water conditions, is tomorrow. As we approach the dry spring and summer months, the scope and severity of California’s drought will become more apparent, but it is already clear that California is faced with extraordinarily dry conditions, with impacts to all sectors and every corner of the state.
As part of the Pacific Institute’s Drought Response efforts, here is the March 31st update of the key information and graphics that characterize the current…
Peter Sinclair has tackled this difficult topic with an excellent video and informative blog post. The blog post is here, and I've pasted the video below.
This is a complicated issue. The water problem in California is obviously made worse by increased demands from population growth and expansion of agriculture. Under "normal" (natural) conditions, California and the American Southwest is fairly dry and can undergo extra dry periods. But climate change seems to be playing a role here as well. It appears that recent lack of rain in the region is the result of changes in atmospheric…
In the last few months, as the severe California drought has garnered attention among scientists, policymakers, and media, there has been a growing debate about the links between the drought and climate change. The debate has been marked by considerable controversy, confusion, and opaqueness.
The confusion stems from the failure of some scientists, bloggers, reporters, and others to distinguish among three separate questions. All three questions are scientifically interesting. But the three are different in their nuance, their importance to policy, and their interest to politicians and water…
The following is also found HERE on the White House web site. I provide it here without comment because it speaks for itself. But if you want more, check out "Global warming action: good or bad for the poor?" by John Abraham, and "Keeping The Carbon In The Ground Elsewhere: Developing Nations" by me.
Drought and Global Climate Change: An Analysis of Statements by Roger Pielke Jr
John P. Holdren, 28 February 2014
Introduction
In the question and answer period following my February 25 testimony on the Administration’s Climate Action Plan before the Oversight Subcommittee of the U.S. Senate’…
If water had its way, this is what California would look like:
Think about it for a second. Every single moment, currents of air move, slowly or rapidly, across every land surface on the planet. Anything loose gets blown slowly or rapidly, to lower places. Every now and then, in some places rarely and in other places commonly, liquid water falls from the sky on almost every land surface on the planet. Now and then, in certain limited areas, frozen water builds up to great heights, thousands of feet hight, and moves along, scraping deep hollows and grooves the size of big lakes out of…
Droughts – especially severe droughts – are terribly damaging events. The human and ecosystem costs can be enormous, as we may relearn during the current California drought.
But they are also opportunities – a chance to put in place new, innovative water policies that are not discussed or implemented during wet or normal years.
In the hopes that California’s warring water warriors open their minds to policy reform, here are some of the issues that should be on the table now, in what could be the worst drought in California’s modern history. But here is what I fear, said best by John Steinbeck…
It is time to recognize the serious California drought for what it is: a bellwether of things to come; a harbinger of even more serious challenges to California water resources allocation, management, and use.
The drought could end next month. It could go on for more years. But it will not be the last drought and it is vital that we take the opportunity -- amidst the serious problems farmers, cities, and the environment all face -- to rethink those aspects of California water policy created in the 1900s and 2000s that no longer make sense in the 21st century.
We must also consider this…
The drought in California is really bad. Bad enough that people are struggling to describe it.
People often equate California with other countries because it is so big and important. "If California was a country, it would be the Nth largest country that does XYZ." It will be interesting to see how this trope works out should the drought continue (and by continue, I mean worsen, because a drought that continues is a worsening drought). "If California was a country, it would have an Arab Spring Uprising." "If California was a country, it would require food aid from the UN." "If…