cobe
"The radiation left over from the Big Bang is the same as that in your microwave oven but very much less powerful. It would heat your pizza only to -271.3°C, not much good for defrosting the pizza, let alone cooking it." -Stephen Hawking
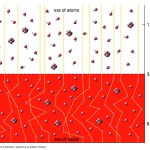
One of the most powerful predictions of the Big Bang -- the fact that our cold, star-and-galaxy-rich, slowly-expanding Universe came from a hot, dense, much more homogeneous state -- was the existence of a bath of leftover radiation that should be detectable, even today.
Image credit: Pearson / Addison Wesley, retrieved from Jill Bechtold.
Back when the…
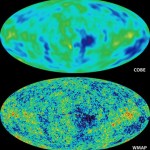
The cosmic microwave background is the radiation left over from the big bang. It's very uniform, 2.725 Kelvin everywhere. We're moving with respect to it, so there's a doppler shift, and we see that as a dipole moment in the Temperature. When we subtract that out, we see variations on the order of 30 microKelvins! WMAP is a satellite (Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe) that measured these anisotropies, and they just released its year 5 data. First off, with the uniform and dipole parts subtracted out, and with the foreground from the galaxy also taken out, here's the map of the microwave…
Alright, startswithabang-ers, Ben, my most avid commenter, saw me online while I was eating breakfast this morning, and pointed me to this new press release. Now, before you get started clicking on everything, the guy who the release is about is Brian Gaensler, who's a really nice guy, lives in Australia, whom I met at the AAS (American Astronomical Society) meeting in Austin, TX last month. Bryan's also brilliant.
Basically, what he did was he said, "well, we know what the rough density of hot gas in our galaxy is, and we can measure the timing of these pulsars to extraordinary accuracy."…
I got a great question earlier today from my buddy Zrinka, and decided to figure out the answer for her, and also for myself. She asks:
Ethan, is it possible to know, or better to say to imagine somehow how our galaxy looks from outside?
What a simple-sounding question! After all, we know what the Earth looks like from the outside: we just go outside of it and photograph it. But the galaxy is too big to do that to; it would take tens of thousands of years moving at the speed of light to get that far away! So we're left with the option of looking at our galaxy from inside of it, and trying to…