Democratic Primaries
As you know, I’ve been running a model to predict the outcomes of upcoming Democratic Primary contests. The model has change over time, as described below, but has always been pretty accurate. Here, I present the final, last, ultimate version of the model, covering the final contests coming up in June.
Why predict primaries and caucuses?
Predicting primaries and caucuses is annoying to some people. Why not just let people vote? Polls predict primaries and caucuses, and people get annoyed at polls.
But there are good reasons to make these predictions. Campaign managers might want to have…
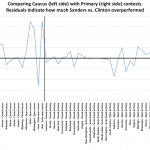
Bernie Sanders has either stated or implied two features that make up his strategy to win the Democratic nomination to be the party's candidate for President this November.
Implied, sort of stated: Convince so-called "Superdelegates" (properly called "uncommitted delegates") in states where he has won to vote for him, even if he is in second. That is a good idea, and if the two candidates are close, it could happen. However, when I run the numbers, giving Bernie "his" uncommitted delegates and Hillary "her" uncommitted delegates, it is pretty much a wash. The uncommitted delegates are not…
This post was written in two parts, pre-primary and post-primary. To see the result and a discussion of what they mean, skip down to the last part of the post, where I'll discuss why Tuesday's results may mean that Sanders could win the primary.
Pre-Primary
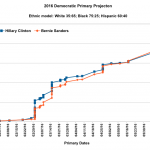
As already discussed, Clinton is likely to win the Democratic nomination. Sanders is too far behind to catch up without extraordinary results, as outlined here. However, it is also true that Sanders is likely to win a majority of contests from here on out, while at the same time, Clinton is likely to win many (if not most?) of the actual…
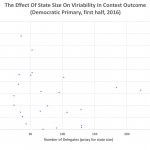
I developed a predictive model for the Democratic primaries that was designed to have the following features:
1) It does not rely on polling;
2) It does use exit polling and other information to set certain parameters;
3) It mainly uses prior primary or caucus results to predict the future, and thus assumes that the status quo is the best indicator.
4) It calculates likely voting patterns based on ethnicity (White, African American, Hispanic), and using likely Democratic party distribution among these groups to predict each contest's outcome.
That method outperformed most other predictions…