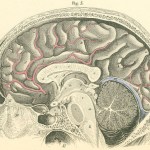
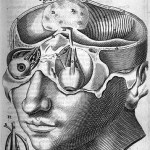
In the 21st century, immortality beckons from several directions: cybernetics, artificial intelligence, telomere extension and cell therapy, maybe even an afterlife. But most of humanity's hope to transcend death revolves around the brain, as the manifestation of our memories and personality. On Pharyngula, PZ Myers considers the merits of new efforts to master the brain, such as a "cryonic brain preservation technique" that promises to preserve your dead gray matter for a future generation. PZ used to prepare tissue for microscopy in the same way: "I was chemically nuking all the proteins in…
neuroscience
In 1817, Karl August Weinhold had a go at a real-life Frankenstein's monster -- only in his version he uses a cat. The German scooped out the brain and spinal cord of a recently dead cat. He then pured a molten mixture of zinc and silver into the skull and spinal cavity. He was attempting to make the two metals work like an electric pile, or battery, inside the unfortunate cate, replacing the electrical of the nerves. Weinhold reported that the cat was revived momentarily by the currents and stood up and stretched in a rather robotic fashion!
It's Alive!!!!
Weinhold's reanimated cat was…
With 2001 in the rear-view mirror, there have been no little green men, no meal-replacement pills, no flying automobiles, no space odysseys. But as big-budget plans to model the human brain prove, proponents of artificial intelligence remain hopeful. In its most literal sense, AI exists already: encoded and executed, endowed with sensors, lenses and microphones, connected to the internet, and stuck in your pocket. But how intelligent does a machine have to be before our worst nightmares come true? Intelligent enough to pass a Turing test? Intelligent enough to nuke the human race? And/or…
Last week, everyone's favorite woo-meister, the man whose woo is so strong that I even coined a term for it way back in the early mists of time (at least as far as this blog is concerned), was woo-fully whining about all those allegedly nasty skeptics on Wikipedia. Yes, Deepak Chopra was clutching his pearls and getting all huffy because, according to him, a group of skeptics known as the Guerilla Skeptics was actually applying science and reason to the Wikipedia entry for his good buddy Rupert Sheldrake. The only problem was, he totally missed the target in that the Guerilla Skeptics…
"My idea of perfect happiness is a healthy family, peace between nations, and all the critics die." -David Mamet
As a theorist in physics, most of my research time is spent looking for errors in painstaking calculations, writing and running simulation code, and trying desperately to connect some very abstract concepts to potential observables in either experiments or the Universe.
But for experimentalists, the key difficulty is always some variation on one unifying theme: getting good data. That's why this weekend, I'm proud to bring you a fantastic takeoff of Daft Punk's Get Lucky by…
I probably don't need to introduce Oliver Sacks to you. You've undoubtedly already delighted over his wobbly affectation and tales of neurological strangeness on RadioLab or NPR. You might have read his lovely first-person account, in the New Yorker, of his early experiments with hallucinogens of all stripes, from the "pharmacological launch pad" of amphetamines and LSD, to the synthetic belladonna-like drug, artane. You may even have read one of his bestselling books of clinical studies, like The Man Who Mistook His Wife for a Hat or Awakenings.
I interviewed Dr. Sacks in 2007, on the…
The history of science can be read as a series of brusque reality checks. Once, we thought the sun revolved around the Earth, but modern astronomy relegated our real estate, incrementally, from the center of everything to a hum-drum corner of an unimportant galaxy in a handful of generations. The theory of Evolution turned us from mini-gods into just a consequence of squicky biological randomness. The decipherment of the structure of DNA and the human genome turned the spark of life into something that can be written down, stored, and analyzed by computers. Again and again, we…
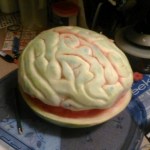
It's time again for fruit and veggie carving season. And what could be better than a carved brain. This time it's out of a watermelon.
Enjoy!
-via Neatorama-
WE all know that bats and dolphins use echolocation to navigate, by producing high frequency bursts of clicks and interpreting the sound waves that bounce off objects in their surroundings. Less well known is that humans can also learn to echolocate. With enough training, people can use this ability to do extraordinary things. Teenager Ben Underwood, who died of cancer in 2009, was one of a small number of blind people to master it. As the clip below shows, he could use echolocation not only to navigate and avoid obstacles, but also to identify objects, rollerskate and even play video games.…
Skull of Hadrocodium wui. (Image courtesy of Mark Klinger and Zhe-Xi Luo, Carnegie Museum of Natural History)
THE question of how mammals evolved their exceptionally large brains has intrigued researchers for years, and although many ideas have been put forward, none has provided a clear answer. Now a team of palaeontologists suggests that the mammalian brain evolved in three distinct stages, the first of which was driven by an improvement in the sense of smell. Their evidence, published in tomorrow's issue of Science, comes from two fossilized skulls, each measuring little more than 1cm in…
Nifty Fifty Speaker Carl Zimmer is often called one of the nation's most astute, informed and lyrical science writers. Specializing in communicating about the wonders and mysteries of evolution, biology and neuroscience, Carl Zimmer - in such books as The Tangled Bank, Parasite Rex, and Soul Made Flesh - writes with such grace, skill and clarity that he makes even difficult subjects like natural selection and the brain understandable and exciting to readers who have little formal education in science.
"I like to write books about subjects that greatly intrigue me --subjects that I want to…
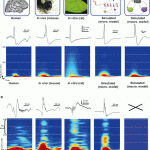
THE patterns of brain waves that occur during sleep can predict the likelihood that dreams will be successfully recalled upon waking up, according to a new study published in the Journal of Neuroscience. The research provides the first evidence of a 'signature' pattern of brain activity associated with dream recall. It also provides further insight into the brain mechanisms underlying dreaming, and into the relationship between our dreams and our memories.
Cristina Marzano of the Sleep Psychophysiology Laboratory at the University of Rome and her colleagues recruited 65 students,…
Daniel Margulies of the NeuroBureau, an open neuroscience community, shared this opportunity:
The Brain-Art Competition 2011
Submission Deadline: 11:59PM CDT, Sunday, June 5th, 2011
Award Notification: June 28th, 9PM at the Cirque du Cerveau Gala (OHBM Annual Meeting), Musée National des Beaux-Arts du Québec.
In order to recognize the beauty and creativity of artistic renderings emerging from the neuroimaging community, we are launching the first annual Brain-Art Competition. Countless hours are devoted to the creation of informative visualizations for communicating neuroscientific findings…
YOUR brain has a remarkable ability to extract and process biological cues from the deluge of visual information. It is highly sensitive to the movements of living things, especially those of other people - so much so that it conjures the illusion of movement from a picture of a moving body. Although static, such pictures trigger dynamic representations of the body, 'motor images' containing information about movement kinematics and timing. Researchers at the Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience in London now show that biological motion is processed unconsciously, and that the speed of…
And you can too! All you have to do is win this gorilla costume. This is guaranteed to work in a women's locker room*. I can't vouch for its success rate in men's locker rooms since.. well... I don't really have to sneak in there. Anyway, all you have to do to have a chance of winning this amazing gorilla suit is to pre-order the new paper back version of Dan Simons' and Chris Chabris' book The Invisible Gorilla.
If you're not into sick horrible ideas like sneaking into locker rooms (because clearly, that is the only thing you could possibly do with that costume) you could also pre-order…
Now this is just cruel: yesterday the Cambridge Science Festival kicked off - a week of science, sciart, sci-journalism and sci-education activities at MIT, Harvard, the Museum of Science, and surrounds. Am I going to be hanging out all day with my fellow-geeks in the sun (which finally came out a few days ago, right on cue)? No! Because I have to write two final papers. (At least they're about sci-law. . . )
Anyway, don't be like me. If you're in the Cambridge/Boston area, have a life and check out the Cambridge Science Festival schedule. There are talks, performances, screenings, panels,…
I was digging through some of my old blog posts and had almost totally forgot about this artwork I commissioned for the blog when I first started back on blogger. Check it out and then I'll fill you in on what I've been up to and why I've been so sparse over the last many months.
I stopped blogging consistently a while back, and it was for a great reason, I promise!
About a year ago, after I passed my prelims, I went on the job market. I interviewed for a couple academic positions (mainly liberal arts) and a number of industry/government jobs. I finally decided to 'sell out' and take the…
"Reasoning was not designed to pursue the truth. Reasoning was designed by evolution to help us win arguments."
- Jonathan Haidt, "The New Science of Morality",
invoking the work of H. Mercier and D. Sperber.
(the whole talk is really interesting).
I've been remiss in not recommending my temporary Scienceblogs scibling "Art and Science Learning" to those of you who are, like me, interested in the sciart intersection. However, I have to say I am not 100% behind its latest (and quite popular post), by Robert Root-Bernstein. It starts,
Most people are at a loss to be able to identify any useful connections between arts and sciences. This ignorance is appalling.
Hmmm. Do you think that's really true, much less "appalling"?
I'm not so sure. I do think it's true that people tend to view arts and sciences as distinct disciplines, which is…