papers
Noise obscures meaningful information. Noise is what ruins your carefully designed synthetic biology gene circuit. But noise is part of life and life, it turns out, needs noise. There's a terrific review article in this week's Nature discussing recent theoretical and experimental work on biological noise showing functional roles for molecular, genetic, and evolutionary noise.
From the abstract:
The genetic circuits that regulate cellular functions are subject to stochastic fluctuations, or 'noise', in the levels of their components. Noise, far from just a nuisance, has begun to be…
Cells are constantly jibber jabbering, sending messages to each other to coordinate behavior, both within a population of single-celled organisms or between cells of an individual multicellular organism. Most of these signals are chemicals that float around in the liquid that surrounds the cells but there recently has been an increased appreciation for cells' sense of "smell"--how cells respond to chemicals that are present as gasses.
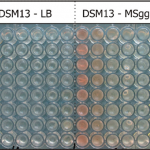
A brand new paper outlines the discovery of "olfaction" in a species of bacteria, Bacillus licheniformis. Trying to save space on a 96 well dish by putting…
A lot of synthetic biology is about getting biology to be more like electrical engineering, designing genetic "logic gates" to create a living circuit board. Beyond analogies, however, cells have many fascinating electrical properties--proteins that transfer electrons like wires, membranes that separate ions and create an electrical charge that drives the metabolism of the cell, channels through these membranes that open and close to activate an electro-biological response. Electrons are electrons whether they are in proteins or copper wires, and many scientists have designed ways to connect…
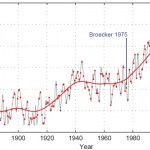
This is not a reference to the recent three decades of rapidly increasing global temperatures, rather it is a reference to an aniversary of the first appearance of the term "global warming" in the peer reviewed literature. The paper was by Wally Broeker and titled "Are we on the brink of a pronounced global warming?"
Real Climate has an interesting post on the details of this paper. The short version is that despite numerous considerations in the paper that have played out differently than hypothesized, the overall prediction of temperature by the end of the 20th century was remarkably…
Geoengineering is getting more and more attention in political discussions as well as research. I am by no means a proponent of any geoengineering scheme I have heard of and the majority of them try to address surface temperature only and therefore do nothing about "the other CO2 problem", aka ocean acidification.
I must confess that H. E. Taylor's article a while back went some way in convincing me that like it or not we need to be considering these perilous pathways. He basically makes the compelling argument that we are in fact now, unwittingly or not, geoengineering our global climate…
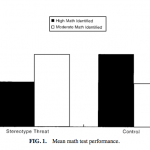
In the recent articles, blog posts, and comment threads about possible biological reasons for the continued gender disparity in tenured math and science faculty positions, the discussion seems to be divided between two groups: those who emphasize the social and cultural aspects involved in gender and intelligence, and those who emphasize the scientific evidence of standardized test performance. The science team rails against "political correctness," claiming that by questioning the merits and motives of scientific hypotheses of differences in innate intelligence between different groups of…
Chris S recently posted a lengthy comment, an extended excerpt from a recent Proceedings of the Royal Society paper. Full citation is: Solar change and climate: an update in the light of the current exceptional solar minimum
Mike Lockwood
Proc. R. Soc. A 8 February 2010 vol. 466 no. 2114 303-329
The abstract is here.
It makes for a very interesting read with lots to think about so I though I would promote it to a post of its own....
The history of science reveals a series of 'controversies'. These often develop into a state where there is little debate within the relevant academic…
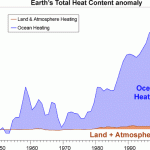
A new study came out in Nature a couple of weeks ago that assesses multiple records of ocean temperatures over the last couple of decades and finds that there is "a statistically significant linear warming trend for 1993-2008 of 0.64âWâm-2".
The challenge the paper took on was one of assessing the uncertainties and inconsistencies in the various records. The paper is Lyman, J.L., et al. 2010. Robust warming of the global upper ocean. Nature 465 and Real Climate had an article about it here.
Also in that issue of Nature is an article by Kevin Trenbreth [PDF] that discusses that paper and…
Light interacts with and controls biological systems in diverse and fascinating ways. Our eyes are made up of thousands of cells that respond to light, sending signals to our brain as light in different colors and shapes moves across them. Photosynthetic cells are full of receptors that can sense and respond to many wavelengths of light, allowing cells to absorb light for photosynthesis, but also to move towards areas of more sunlight and know when the seasons are changing. Synthetic biology takes these light-responsive systems as parts that can be recombined, shuffled and integrated into…
My two great thesis project loves are hydrogen and symbiosis, and as such, the recent news of a multicellular organism that lives in a completely oxygen free environment and gets its energy from hydrogenosomes instead of mitochondria is totally fascinating.
Hydrogenosomes are organelles that are evolutionarily related to mitochondria. Mitochondria generate energy for the cell by transferring electrons pulled off of sugars molecules to oxygen (this is why we breathe oxygen). The energy from this electron motion is transferred to the production of ATP, the energy currency of the cell, through…
An interesting paper in BioEssays last month looks at the potential future of xenobiology, totally orthologous biological systems made out of synthetic nucleotide and amino acid bases, new cells that use XNA instead of DNA. The author, Markus Schmidt, argues that while the design of such systems current poses a difficult technological challenge to researchers in synthetic biology, that xenobiological systems will enable a "genetic firewall" between natural and designed organisms, creating a built-in measure of biosafety.
This is something I've argued for before, in reference to creating new…
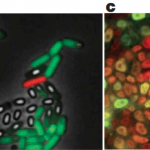
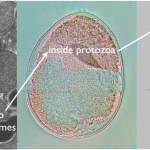
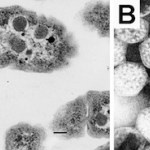
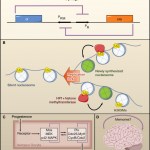
Carboxysomes are small compartments inside photosynthetic bacteria where the machinery for capturing carbon dioxide is concentrated. You can see carboxysomes and their characteristic virus-like shape when you look at slices of these bacteria under an electron microscope:
Until recently, no one had looked at carboxysomes under the microscope in cells that were still alive. My labmates Dave and Bruno developed a way to label carboxysomes with fluorescent proteins and track them under a microscope as the cells grow, and their amazing paper in Science details some of the fascinating systems they…
From up north, we have some more troubling news. Actually very troubling. Catastophic release of methane hydrates is a prime suspect in a few events dramatic enough to show in the earth's geological records, coarse and obscured as that record may be. (Our actions today will be featured prominently in that record for anyone looking back a million years from now.) It has been a worry for many years that humanity is running the risk of triggering such a release again, which would truly pile disaster on top of calamity.
New research coming out in Science today indicates that this most dire of…
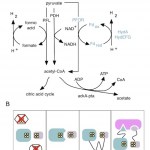
My paper, "Insulation of a synthetic hydrogen metabolism circuit in bacteria" just came out in the Journal of Biological Engineering! And it's open access!
We designed a metabolic circuit in bacteria that produces hydrogen (a potentially useful fuel) from natural precursors in the cell. The proteins in our synthetic pathway work to make hydrogen by transferring high-energy electrons from pyruvate, a common metabolite, to protons that are freely floating in the watery cytoplasm. The electrons transfer between the proteins through quantum-mechanical tunneling, which makes hydrogenases and…
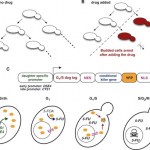
My labmate Bruno's newest paper, "A synthetic circuit for selectively arresting daughter cells to create aging populations" came out today in the journal Nucleic Acids Research (and it's open access!). Using a cleverly designed genetic circuit that activates cell growth arrest in newly divided cells only in the presence of a drug, Bruno was able to create a population of yeast made up of only old cells, called the "daughter arrester."
You would think that yeast, being so single celled and bread-y, wouldn't be able to tell us much about human biology or anything as complex as aging, but many…
Today in my searches for the hot new trends in synthetic biology, I found a news article from Science Daily with an intriguing title: "Scientists Achieve First Rewire of Genetic Switches." Rewiring genetic switches sounds pretty neat, but this headline was intriguing to me first of all because it's kind of late to the party--in fact one of the first papers in modern synthetic biology back in 2000 was about engineered genetic switches: "Construction of a genetic toggle switch in Escherichia coli". When I looked more closely, the article wasn't about this kind of transcriptional switch though,…
Cooperation and altruism are widespread in biology, from molecules and genes working together in a cell, to bacterial communities that require coordinated behavior to survive in a tough environment, to human relationships and societies. Our human cultural perspective (perhaps even more specifically our American cultural perspective, focused as it is on individuality, free markets, and the American Dream), however, treats cooperation as an outright anomaly that has to be explained away by science (or often, religion). If natural selection is about the "survival of the fittest" how can a…
My friend Devin's essay, "Making Cellular Memories" just came out today in Cell (and it's open access!) It's a great look at how natural cells and synthetic biological systems use feedback loops in order to maintain memory of past events. Like whole animals, cells need to remember what happened to them before in order to respond appropriately to new signals. Synthetic biologists can use memory to track cells that have experienced a certain input in a heterogeneous population, and to activate different responses depending on the historical context.
In sum, both nature's wisdom and previously…
This press release was forwarded to me:
WASHINGTON-- A new study published today in the Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) shows that refrigerant chemicals, so
called F-gases, are a more dangerous global warming threat than previously
predicted. The study was authored by scientists from the
Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency, United States government
agencies NOAA and EPA, along with a scientist from the chemical company
Dupont.
The paper projects that HFC (hydrofluorocarbon) emissions will rise
rapidly in coming years and decades, threatening to effectively…
Nature magazine recently published a paper showing that Antarctica has actually been warming about .1oC/decade since the 1950's. It was the cover story:
A new reconstruction of Antarctic surface temperature trends for 1957-2006, reported this week by Steig et al., suggests that overall the continent is warming by about 0.1 °C per decade. The cover illustrates the geographic extent of warming, with the 'hotspot' peninsula and West Antarctica shown red against the white ice-covered ocean.
That the antarctic seemed to be slightly cooling despite elevated greenhouse gas levels has been a…