virus
Photo of sea sponges by Steve Rupp, National Science Foundation via Wikimedia Commons
Through the course of evolution vertebrates have apparently lost their gene-encoded viral defense mechanisms. These ancient defenses allow plants and insects to silence the expression of certain genes by using what is known as RNA interference. This natural defense system can be manipulated to create genetically modified crops that resist certain infections. However, a new study by researchers from the University of Leuven in Belgium examined over 40 organisms in search of a specific family of proteins…
Check out this video from Reuters (via YouTube). It summarizes an exciting study from researchers at Imperial College London who were able to stop the progression of Alzheimer's disease in mice by administering a modified virus to the animals. The virus worked by preventing the formation of the characteristic amyloid plaques that are responsible for causing damage to neurons in the brain. Importantly, the virus did not result in loss of existing brain cells. It will be interesting to see how this research progresses and whether the treatment will not only be safe, but effective for humans…
If there's one thing that's frustrating about the U.S. justice system, it's just how slow the wheels of justice grind. For example, it's hard to believe that it was over two years ago that "pH Miracle" quack Robert O. Young was arrested for fraud, grand theft, and practicing medicine without a license, producing one of my favorite images ever on this blog, that of Young in a blue prison jump suit. The only way it could have been better would have been if it had been an orange jumpsuit, but unfortunately a contact in San Diego tells me that San Diego County doesn't use orange jumpsuits for its…
CNBC publishes an antivaccine press release from the Weston A. Price Foundation and Leslie Manookian
One of the things I've noticed over the last decade of covering pseudoscience and quackery from a skeptical point of view is that no pseudoscientific trope ever really dies. This is particularly true of antivaccine tropes. No matter how many times this piece or that of antivaccine misinformation is slapped down, sooner or later it always resurfaces. Indeed, I remember one article that I've seen resurface on several occasions that inevitably bears a title that is some variation of a statement that a "new study vindicates Andrew Wakefield." Every time that article pops up, various antivaccine…
Varroa mites can be highly destructive to bee colonies and are a big concern for beekeepers. They get inside honeycombs where they lay eggs and feed on the bee pupae. When the adult bees are released from their cells, so are the mites, which then go on to lay more eggs. Bees that live with these mites are usually smaller and prone to a disease known as deformed wing virus. The presence of the mites and the disease can decimate an entire hive.
Image of Varroa mite on a honeybee from Wikipedia
Dr. Francis Ratnieks (University of Sussex, Brighton) observed 42 honeybee colonies and discovered…
I've been asked several times about this NY Post article on the CDC's "admission" that a sneeze could spread Ebola. The Post (which, I should note, is the least credible newspaper in New York City, for those not familiar with the paper) suggests that the CDC has changed their tune regarding the spread of Ebola.
Except, they haven't, and this is a ridiculous, trumped-up non-story, passed along not only by the Post but by others of the typical suspects like conspiracy theorist extraordinaire Mike Adams, aka "The Health Ranger" of Natural News.
Here's what the NY Post claims:
“Droplet spread…
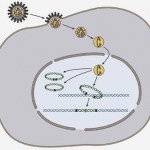
Depiction of a retrovirus integrating its DNA into the DNA of the host cell. Image from: http://bit.ly/1phzpbR
I read an interesting article in Scientific American that discussed the so-called Peto's Paradox. Dr. Richard Peto (University of Oxford) came up with the idea that if every cell has an equal probability of becoming cancerous, then larger animals would be predicted to develop cancer at higher rates than smaller animals. As it turns out, it is not that simple. All mammals exhibit similar cancer rates, with some exceptions. This is what came to be known as Peto's Paradox.
Some…
(As previously, spoilers abound)
So on this week's Walking Dead soap opera, we find that Daryl/Michonne's group is still out and about searching for medical supplies. Back at the prison, the food situation is dire (apparently all the food stores were in the cell block where the infection broke out), so Rick and Carol head out to look for both medicines and food from the local 'burbs. During their outing, discussion ensues of Carol's attempt to stop the prison's apparent influenza outbreak by killing two people who, at that point, were the only ones showing symptoms of disease. Rick decides he…
Image of Indian Flying Fox from Wikipedia, Fritz Geller-Grimm
An ambititous project seeks to identify all unknown viruses in mammals to determine the relative risk of infection to humans and to develop strategies to prevent and treat infections before they become pandemics. The pioneering research team is led by Dr. Simon Anthony at Columbia University and Dr. Peter Daszak from EcoHealth Alliance.
The team started by looking for viral infections in the Indian flying fox (Pteropus giganteus), a species with pathogens known to transfer to humans (Nipah and Hendra viruses). Over five…
A virus is to blame for the deaths of hundreds of bottlenose dolphins along the East Coast of the United States:
A couple of weeks ago, I was horrified to learn of a new "biomed" treatment that has been apparently gaining popularity in autism circles. Actually, it's not just autism circles in which this treatment is being promoted. Before the "autism biomed" movement discovered it, this particular variety of "miracle cure" has been touted as a treatment for cancer, AIDS, hepatitis A,B and C, malaria, herpes, TB, and who knows what else. I'm referring to something called MMS, which stands for "miracle mineral solution." As I pointed out when I discovered its promotion for various maladies and then later…
By Mark Pendergrast
As I watched the blockbuster bio-thriller Contagion, I was struck by how realistic it was in many ways. That isn't surprising, since many epidemiologists, including those from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in Atlanta, served as advisors. The film was based on a simple premise. What if a new, deadly virus that kills one out of four people it infects were also easily transmissible from human to human?
I knew more about the subject than most people in the audience, because I spent five years researching and writing Inside the Outbreaks, a history…
Ebola has long been associated with wildlife. From the early days, bats were viewed as a potential reservoir (though it wasn't confirmed that they actually harbored the virus until 2005). Contact with wild animals--particularly primates which were butchered for food--was also long thought to be a risk factor, and now we know that primates can become ill with Ebola and pass the virus to humans.
What hadn't been examined until 2008 were pigs. I mean, it's not exactly the animal you associate with central Africa, where many of the Ebola cases have been concentrated. However, pigs are much more…
At his new digs, PalMD discusses recent news revealing the presence of dengue virus in the Florida Keys--the first appearance in the state in almost 75 years. Dengue is a mosquito-borne virus that can cause serious disease, including a hemorrhagic manifestation, and the current outbreak is pitting public health professionals against the tourism industry in the Keys. It's also brought to public attention the closing of CDC's vector-borne disease branch due to funding difficulties. The intersection of these--viral emergence, politics, and economic interests--has the potential to cause a huge…
Mark Pendergrast writes: To kick off this book club discussion of Inside the Outbreaks, I thought I would explain briefly how I came to write the book and then suggest some possible topics for discussion.
The origin of the book goes back to an email I got in 2004 from my old high school and college friend, Andy Vernon, who wrote that I should consider writing the history of the EIS. I emailed back to say that I was honored, but what was the EIS? I had never heard of it. I knew Andy worked on tuberculosis at the CDC, but I didn't know that he had been a state-based EIS officer from 1978…
Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) is a disease that afflicts people with extreme and debilitating tiredness that lasts for many years and isn't relieved by rest. Some estimates suggest that it affects up to 1% of the world's population. We don't know what causes it. Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers in the world and kills around 221,000 people every year. Its causes too are largely unknown. What do these two diseases have in common? They have both been recently linked to a virus called XMRV (or xenotropic MulV-related virus in full).
This doesn't mean that you can 'catch' either…
Since late 2006, honeybees in Europe and North America have been mysteriously disappearing. Once abuzz with activity, hives suddenly turned into honeycombed Marie Celestes. They still had plentiful supplies of honey, pollen and youngsters but the adult workers vanished with no traces of their bodies. The phenomenon has been dubbed colony collapse disorder (CCD). In the first winter when it struck, US hive populations crashed by 23% and in the next winter, they fell again by a further 36%.
Eager to avert the economic catastrophe that a bee-less world, scientists have been trying to find the…
This article is reposted from the old Wordpress incarnation of Not Exactly Rocket Science. There's been more work on CCD since, but I'm reposting this mainly because of some interesting follow-up research that will I will post about tomorrow.
In 2006, American and European beekeepers started noticing a strange and worrying trend - their bees were disappearing. Their hives, usually abuzz with activity, were emptying. There were no traces of the workers or their corpses either in or around the ghost hives, which still contained larvae and plentiful stores of food. It seemed that entire…
Viruses and bacteria often act as parasites, infecting a host, reproducing at its expense and causing disease and death. But not always - sometimes, their infections are positively beneficial and on rare occasions, they can actually defend their hosts from parasitism rather than playing the role themselves.
In the body of one species of aphid, a bacterium and a virus have formed a unlikely partnership to defend their host from a lethal wasp called Aphidius ervi. The wasp turns aphids into living larders for its larvae, laying eggs inside unfortunate animals that are eventually eaten from…