viruses
Typically when we think of flying things and influenza viruses, the first images that come to mind are wild waterfowl. Waterbirds are reservoirs for an enormous diversity of influenza viruses, and are the ultimate origin of all known flu viruses. In birds, the virus replicates in the intestinal tract, and can be spread to other animals (including humans) via fecal material.
However, a new paper expands a chapter on another family of flying animals within the influenza story: bats.
I've written previously about the enormous diversity of microbes that bats possess. This shouldn't be…
As I mentioned yesterday, the epidemiology of hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) was murky for several decades after it was first defined in the literature in 1955. In the ensuing decades, HUS was associated with a number of infectious agents, leading to the general belief that it was a "multifactorial disease"--one that had components of genetics and environment, much like we think of multiple sclerosis today, for example.
Several HUS outbreaks made people think twice about that assumption, and look deeper into a potential infectious cause. A 1966 paper documented the first identified outbreak…
Or maybe wild-ass speculation. As the data continue to come in about the E. coli outbreak in Germany caused by E. coli O104:H4 HUSEC041 (well, everything but the public health and epidemiological data which are a contradictory, incoherent mess), it appears that one of the things that has made this strain so dangerous is its ability to make Shiga-like toxin--a compound that stops cells from making proteins cells--the mechanism is similar to that of the biowarfare agent ricin (Note: there are several different Shiga-like toxins; for clarity, since it's not germane to this post, I'll lump…
When I first saw the title of this PloSOne article, "Unauthorized Horizontal Spread in the Laboratory Environment: The Tactics of Lula, a Temperate Lambdoid Bacteriophage of Escherichia coli", I thought, "Hunh?!? You can actually publish articles about laboratory contamination?", but it's actually a very interesting article. In short, the article describes the discovery of a bacteriophage ('phage')--a bacterial virus--that is very well suited for survival and spread in microbiology laboratories.
To be successful, Lula faces several problems:
1) It has to successfully hide from researchers…
tags: HIV and 'Flu -- The Vaccine Strategy, microbiology, epidemiology, virology, vaccines, medicine, public health, viruses, influenza, HIV, Seth Berkley, TEDTalks, TED Talks, streaming video
Seth Berkley explains how smart advances in vaccine design, production and distribution are bringing us closer than ever to eliminating a host of global threats -- from AIDS to malaria to flu pandemics.
TEDTalks is a daily video podcast of the best talks and performances from the TED Conference, where the world's leading thinkers and doers give the talk of their lives in 18 minutes. Featured speakers…
Are aliens little green men of unpredictable motives? Horrible insect-like face-hugging, chest-exploding monsters? Are they super-smart, super-slimy, super-fishy, body-cavity-probing, disc-flying creatures, searching for planets to colonize and people to destroy as Stephen Hawking warned, or are they something much more mundane? Could there be alien life already on earth, too microscopic, too different to notice? Could life on earth have been seeded from an alien land, with secret messages encoded in our DNA? We've been scanning the sky for extraterrestrial radio signals for years, should we…
Student guest post by Andrew Behan
Malignant Mesothelioma (MM) is a rare type of cancer which manifests itself in the thin cells lining the human body's internal organs. There are three types of MM; pleural mesothelioma, peritoneal mesothelioma, and pericardial mesothelioma, affecting the lining of the lungs, abdominal cavity, and lining of the heart, respectively (1). Pleural mesothelioma is most common, consisting of about 70% of all MM cases and has a poor prognosis; patients live a median time of 18 months after diagnosis. (Note: for the purposes of this article, MM will be used to…
Student guest post by Zainab Khan
Schizophrenia has puzzled and often times scared not only the scientific community, but also the general public since its emergence. Cases of schizophrenia-like behavior have been well documented in history. As this disease has been studied, factors such as genetics, environment, and even personal habits have all been associated to some degree with schizophrenia. However, evidence in past years has mounted showing an association between infectious agents and schizophrenia. The three main infections associated/studied with schizophrenia have been…
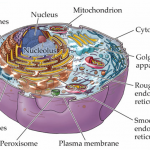
Animal cells are made up of many smaller membrane-bound compartments called organelles that perform highly specialized functions necessary for life. Incredibly, several of these organelles have been shown to be evolutionarily related to free-living bacteria, captured and incorporated inside a larger cell billions of years ago in a complex mutually beneficial relationship, known as endosymbiosis (a partnership between two species where one of the species is inside the other). The mitochondria that power our cells, generating energy by breaking down sugars are in fact relatives of regular old…
Sex might be fun but it's not without risks. As your partner exposes themselves to you, they also expose you to whatever bacteria, viruses or parasites they might be carrying. But some animals have a way around that. Ekaterina Litvinova has found that when male mice get a whiff of female odours, their immune systems prepare their airways for attack, increasing their resistance to flu viruses.
Litvinova worked with a group of mice that were exposed to bedding that had previously been soiled by females in the sexually receptive parts of their cycle. She compared them to a second more monastic…
ERV familiarizes us with the different "layers" of the immune system, including intrinsic, innate, and adaptive immunity. The last layer makes specific antibodies to recognize pathogens, but in the case of HIV, capable antibodies aren't enough to stave off the progression of disease. ERV writes, "HIV-1 evolves to escape these antibodies...and your body can't catch up." The high mutability of HIV-1 makes for a very plastic envelope, meaning the virus continually shifts shape and evades the watchful eye of the immune system. In another post, ERV explains that antibodies make diseases like…
While I'm not that big a fan of the project trying to find commonalities between economics and biology, largely because I think explanations of specific phenomena often reduce to those stupid fucking natural history facts, I was struck by this argument by economist Samuel Bowles about the assumption of optimality in the supposed tradeoff between income equality and economic output (italics mine):
Theoryland may be the only place the "equality-efficiency trade-off" really works. Just to prove it wrong, Bowles charts the concept on a whiteboard at SFI.
The vertical axis is economic output. The…
Vaccines have guarded health and life for centuries, relegating once devastating diseases to near total obscurity. But many people now take vaccines for granted, and some blame vaccines for autism and other disorders. On Respectful Insolence, Orac reports the downfall of 1998 research which first tied MMR vaccines to the occurrence of autism in children. As Orac writes, "hearing that the man whose bad science launched a thousand quackeries had finally been declared unethical and dishonest [...] brought joy to my heart, the joy that comes with seeing justice done." ERV jumps on other news…
Meet your viral ancestors - how bornaviruses have been infiltrating our genomes for 40 million years
Cast your mind back 40 million years and think about your ancestors. You're probably picturing creatures that looked like a bit like today's monkeys, but they're only part of your family tree. To see your other ancestors, you'd have to whip out an imaginary microscope. Meet your great-great-great-etc-grandviruses.
The human genome is littered with the remains of viruses that, in ages past, integrated their genes into the DNA of our ancestors. They became a permanent fixture, passed down from parent to child. Today, these "endogenous retroviruses", or ERVs, make up around 8% of our genome.…
As we shiver in the northern hemisphere, holiday cheer isn't the only thing in the air—there are also flu, cold, and other contenders just waiting to hit a mucous membrane. Revere questions H1N1 terminology on Effect Measure, citing "10,000 deaths, 47 million infections and over 200,000 hospitalizations" caused by the virus, with the "heart of flu season" still to come. On The White Coat Underground, PalMD reports more CDC data, revealing a "death rate from influenza in American Indians/Native Alaskans" that is almost four times the rate of other ethnicities. Rhinovira are also out in…
This is not a needle exchange program center
(from here)
I've written before about the needle exchange legislation which is very good...in an imaginary world lacking parks, schools, and other places where children congregate. From Maine, we find out what this legislation really means:
Such a position could conceivably pave the way for additional federal money for needle exchange -- with one catch. Bill McColl is the political director at AIDS Action in Washington D.C., who's been following the needle exchange debate in Congress. "They did accept an amendment that would ban the use of…
It's not as bad as the Great Brooklyn Tampon Shortage, but it's just become a lot harder to study marine viruses. There are two basic ways to figure out how many viruses are in a given sample, such as a milliliter of seawater. One method is to mix a bacterial (or algal) cell with a certain amount of seawater and look for plaques--holes in the lawn:
(from here)
The number of plaques equals the number of viruses.
This method has several problems, perhaps the most obvious of which is that you will only observe plaques if the virus can infect those cells. A culture-independent method filters…
No, not that stuff (well, actually, yes, that stuff too, but I definitely don't want to know about it). One of the important tools in fighting infectious disease is disinfecting surfaces. Which brings me to a recent paper about cruise ships and cleanliness. In June 2006, 43 norovirus outbreaks occurred on thirteen vessels. Noroviruses can cause severe vomitting and diarrhea, and in children, particularly infants, can be deadly (also see Aetiology). In the paper, the authors decided to examine how often bathroom surfaces on cruise ships are cleaned:
Methods. Trained health care…
For anything? Excluding very rare norovirus outbreaks, I can't remember ever reading about school absentee rates like these from Grafton, MA:
Grafton High School closed early today after more than a third of its students and more than a quarter of its staff stayed home sick. It is the only school in the state to close, according to public health and education departments, but absenteeism has been elevated some communities across the state. At the beginning of the school year, state officials urged schools to close only as a last resort during flu season and instead focus on keeping sick…
Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) is a disease that afflicts people with extreme and debilitating tiredness that lasts for many years and isn't relieved by rest. Some estimates suggest that it affects up to 1% of the world's population. We don't know what causes it. Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers in the world and kills around 221,000 people every year. Its causes too are largely unknown. What do these two diseases have in common? They have both been recently linked to a virus called XMRV (or xenotropic MulV-related virus in full).
This doesn't mean that you can 'catch' either…