Brain and mind
Does the brain really operate like some kind of extra-complex computer, with logic gates and circuits made of the synapses that connect one neuron to another?
In 2009, we wrote:
In the future, the interface between brain and artificial system might be based on nerve cells grown for that purpose. In research that was recently featured on the cover of Nature Physics, Prof. Elisha Moses of the Physics of Complex Systems Department and his former research students Drs. Ofer Feinerman and Assaf Rotem have taken the first step in this direction by creating circuits and logic gates made of live…
Is this science writer jazzed that ninth-grade girls from a religious girls’ school in Jerusalem won a space/science contest? You bet your sweet solar-powered spacelab she is! It is not just that these girls beat out a lot of other classes (over 400), or that they break more than one stereotype. They also came up with a pretty clever idea for studying the Sun: Send a spacecraft to scatter assorted nanolabs all over an asteroid that is about to pass close to the Earth on its way to the Sun. The contest is held every year in memory of Israeli astronaut Ilan Ramon, who went down with the crew of…
“Inclusion bodies – those clumps of protein that are found in the brain cells of Alzheimer’s patients – are, sadly, a product of aging,” says Dr. Maya Schuldiner. “They can form naturally in practically all cells, but when these cells get old, the mechanism for clearing them away starts to fail.”
That is not great news for those of us who are already seeing signs of incipient dementia every time we forget a name or misplace our keys. But of course there is good news too. Schuldiner has discovered a “detergent” that cells make to wash away those nasty protein clumps. And she believes that, in…
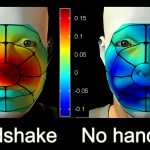
Today's guest blogger is Idan Frumin, a student in the group of Prof. Noam Sobel in the Neurobiology Department. Their research on the transmission of odor compounds while shaking hands appears today in eLife.
It all started one day after lunch, sometime back in 2011. We sat in the lab’s living room (Yeah, we have a living room. And a bedroom. And a blind pet cat. But that’s a different story), when Noam asked – ever wonder why people shake hands?
– To show you don’t have a saber up your sleeve – I immediately retorted.
– But that seems odd, doesn’t it? After all, we’re not in the…
Get rid of your addictions while you sleep? Weizmann Institute researcher Dr. Anat Arzi is not promising this yet, but she and Prof. Noam Sobel have shown that changing bad habits through sleep conditioning could someday be possible. After just one session in the Neurobiology Department’s sleep lab, volunteers reported smoking on average 30% fewer cigarettes over the course of a week.
Volunteers given the same conditioning while awake did not reduce their nicotine consumption.
Arzi and Sobel had first demonstrated true sleep learning in 2012. This is the same conditioning that Pavlov…
Since mental health problems are estimated to affect some 10% of the world’s population, it stands to reason that if you don’t suffer from depression, anxiety or bipolar disorder yourself, you are probably close to someone who does. So you might be pleased to read about a new finding that could eventually lead to a whole new approach to treating this group of common mood disorders.
The finding is that a tiny scrap of RNA – a microRNA that works in the brain – acts as a sort of mood regulator. It works something like the needle in a steam valve. Mice that had high levels of this particular…
Take a bunch of peculiar individuals, put them all together in one setting; film their every move, every second of the day. Sound familiar? Dr. Tali Kimchi is explicit about the resemblance of her experiments to a well-known reality TV show. The difference, of course, is that Kimchi’s subjects are mice. She places large groups of animals in a common pen in her lab, which is fitted out with video cameras, infrared lighting for nighttime filming and electronics to continuously record information from the ID chips implanted in each mouse. And while no one can deny that our enjoyment at seeing…
To attain knowledge, add things every day. To attain wisdom, remove things every day.
Lao Tsu
Apparently our nervous systems develop according to the Chinese philosopher’s principle of being and not being. As our nerve cells grow, they send out long extensions – axons – throughout the developing tissues. And as they reach out, some are also pruned back. The configuration of nerve endings we finally possess depends on both what was added and what was removed.
Which axons will complete their developmental journeys and which will be pruned back? For some, it is simply a matter of fate.
But in…
Weizmann Institute scientists have created a “white smell.” Think about white light or white noise: Each mixes a bunch of different waves together from various parts of the visual or audible spectrum. Those wavelengths combine such that we perceive that unobtrusive light or sound we call “white.”
How do smells fit into this scenario? Prof. Noam Sobel and his group have already shown that smells have their own spectrum – ranging from pleasant to unpleasant – and that this relates to the chemical structure of the odor molecules. Is this spectrum truly analogous to that of light or sound? That…
The idea of “seeing the world through the eyes of a child” takes on new meaning when the observer is a computer. Institute scientists in the Lab for Vision and Robotics Research took their computer right back to babyhood and used it to ask how infants first learn to identify objects in their visual field.
How do you create an algorithm that imitates the earliest learning processes? What do you assume is already hard-wired into the newborn brain, as opposed to the new information it picks up by repeated observation? And finally, how do you get a computer to make that leap from a data-crunching…
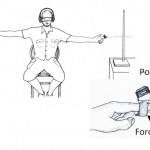
We have been told what it’s like to be a bat or a bird; now Prof. Ehud Ahissar and Dr. Avi Saig are getting people to experience what it’s like to be a rat. Specifically, they want the participants in their studies to learn what it’s like to locate things in the dark by twitching their whiskers.
The point, of course, is not to get humans to pretend they are actually rats, but to see how they learn to sense the world with a new sense. Whisking is a fairly complex sense, involving spatial coordinates – horizontal, vertical and distance from the base of the whisker – and timing. It only works…
The actors on the stage work their magic, turning a few disparate phrases - "challenge, giving birth, infinity, chaos, visiting a new country" - into a brief but charming improvised sketch, to the delight of the audience. But the viewers, filling a large auditorium at the Weizmann Institute of Science, expect more than to be entertained. Since the improvised play is part of a lecture by Prof. Uri Alon, a Molecular Cell Biologist, they know scientific insights are bound to follow.
Indeed. Combining his two passions, science and theater, Alon has recently created a "theater lab" on the…