history of science
This series of sciart wallpapers by Dan Funderburgh were inspired by the Time-Life Science Library, a series of educational books published in the 1960s. For those of us old enough to remember them, Time-Life's series are objects of nostalgia in themselves. Coupling the vintage design and palettes of those books with vintage sci-art symbolism yields a sharply contemporary set of prints.
Funderburgh describes his work as "a repudiation of the fabricated schism between art and decoration;" you could also describe it as a repudiation of the fabricated gulf between science and design. (Fun…
Via iO9, a Nature News slideshow of natural history engravings by physician Martin Lister's teenage daughters, who contributed technically accurate engravings of shells to one of his books, the Historiae Conchyliorum:
Historians now believe the pair were the first women to use microscopes to help produce some of their scientific drawings. Anna and Susanna's place in the history of science is explored in a biography of Martin Lister in preparation by historian Anna Marie Roos of the University of Oxford's Cultures of Knowledge project. In a recent web post, Roos describes how she stumbled…
National Museum of Health & Medicine has an amazing flickrstream of vintage medical photographs and other ephemera. Lately they've been adding diagnostic/documentary photos of Civil War soldiers, as well as some military propaganda posters (anti-VD and anti-food waste, of all things). This series of photos of a lab setup for measuring cranial capacity are my favorites. Check out the handled basket of skulls! And they're using an "insufflator!" I did not even know that was a word.
Happy holidays to our friends at Bottled Monsters and thanks for all the wonderful photos!
This is un freaking real.
My friend John O at Armed With Science has dug up a classic animated film produced for the National Naval Medical Center in 1973. It starts with an awards ceremony for the "Communicable Disease of the Year," hosted by the Grim Reaper (who turns out to know a lot about medical history.)
The top prize is won by the Dracula-esque Count Spirochete (AKA syphilis), over the vociferous objections of a shortlist of other diseases, including smallpox ("I've scarred and disfigured millions of people!") and gonorrhea (who resembles a lavender Tribble with a pitchfork). The…
Diptheria vaccinations in the 1920s
The town of Leicester was a particular hotbed of anti vaccine activity and the site of many anti-vaccine rallies. The local paper described the details of a rally: "An escort was formed, preceded by a banner, to escort a young mother and two men, all of whom had resolved to give themselves up to the police and undergo imprisonment in preference to having their children vaccinated...The three were attended by a numerous crowd...three hearty cheers were given for them, which were renewed with increased vigor as they entered the doors of the police cells."…
After some scrambling, the Eavesmade team (self-described purveyors of "lasercut science goodness") has their scientist ornaments back in stock! And I have my very own beribboned Carl Sagan and Albert Einstein!
Here they are on my mantel; Sagan is on a rocket, and Einstein is pondering time, of course:
Due to popular demand, Eavesmade just added a Nikola Tesla ornament to their collection. So now I need that too. (It would be especially awesome to have a Tesla ornament on one of those vintage aluminum trees. . . )
Thanks, Eavesmade!
I've been dithering about buying these for my scientist friends, but it looks like eavesmade's etsy shop may be running low, so I'm going to quit dithering and just post this for your pre-Cyber Monday enjoyment. They're wooden scientist holiday ornaments, featuring the likes of Carl Sagan, Rosalind Franklin, and Stephen Hawking. I think they're both great and hilariously awkward.
You get six for $30 plus shipping. Order fast. . . . !
PS Thanks to Joanna for the link!
Today's Guardian has a very interesting (though long) article by Richard Holmes, author of The Age of Wonder, about the unsung women of science. In the Guardian piece, Holmes shares some of his research for his forthcoming book, The Lost Women of Victorian Science:
[M]y re-examination of the Royal Society archives during this 350th birthday year has thrown new and unexpected light on the lost women of science. I have tracked down a series of letters, documents and rare publications that begin to fit together to suggest a very different network of support and understanding between the sexes.…
In less than a month (December 2nd), Christie's will auction off Edward Tufte's library - an idiosyncratic collection of first edition books, plates, prints, and ephemera that the dataviz guru calls his "Museum of Cognitive Art," and I call "Jessica's Christmas List."
I'm not going to sample low-rez images of the lots here, because there's a stunning slideshow, complete with curation, at the Christie's website. If you've got ten minutes, this is virtual antiquarian dataviz windowshopping at its best.
There appear to be 160 lots; Tufte's website describes it as "200 rare books, including major…
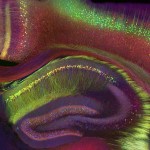
Hippocampus: Broad Overview
Tamily Weissman, Jeff Lichtman, and Joshua Sanes, 2005
from Portraits of the Mind: Visualizing the Brain from Antiquity to the 21st Century by Carl Schoonover
The first time I created a transgenic neuron, it was in a worm, C. elegans -- a tiny, transparent cousin of the earthworm. I injected DNA into the embryonic worm, let it grow up, and voila: there was one eerie green blotch like a little Pac-Man ghost, its long green axon a lime racing stripe running along the worm's transparent body. The worm wiggled, but I was the one hooked: science is beautiful.
You…
I finished Jennifer Ouellette's new book a few weeks ago, shortly after my trip to Alabama, but it's taken me a long time to get around to reviewing it due to a combination of too much work and being a Bad Person. There's finally a tiny break in the storm of work, though, so here's a slightly belated review.
The Calculus Diaries is not a book that will teach you how to do math. There aren't worked examples, detailed derivations, or homework problems in the main text. It might, however, teach you not to fear math, as it provides a witty and accessible explanation of the key concepts behind…
Nick pointed me to a fabulous podcast series by CBC radio called "How To Think About Science." Each episode is a long and fascinating interview with a prominent scholar of science--scientists, philosophers, sociologists, anthropologists, and historians who explore how science is done, how scientists work, and how scientific ideas and facts are communicated. Check it out!
A lot of people have been blogging and Twittering about this subway map of science, which puts various branches of science in the place of the lines on the London Underground map, showing connections between them. It's a huge graphic, but a kind of cool image.
I do, however, have a problem with it, which is illustrated by the key to the lines shown at right. The category of physics is presented as "Theoretical Physics and Quantum Mechanics." I have no problem with the quantum part, as quantum mechanics is one of the greatest intellectual achievements in human history. I do have a problem…
Over at Unqualified Offerings, Thoreau proposes an an experimental test of Murphy's Law using the lottery. While amusing, it's ultimately flawed-- Murphy's Law is something of the form:
Anything that can go wrong, will.
Accordingly, it can only properly be applied to situations in which there is a reasonable expectation of success, unless something goes wrong. The odds of winning the lottery are sufficiently low that Murphy's Law doesn't come into play-- you have no reasonable expectation of picking the winning lottery numbers, so there's no need for anything to "go wrong" in order for you…
Over in yesterday's communications skills post commenter Paul raises a question about priorities:
I wonder to what extent good writers, public speakers and communicators are being promoted in science in place of good thinkers - people who can challenge prevailing dogma, invent promising novel approaches to old problems, and who have the intuition needed for deducing correct theories from just a few observations.
I think of this as the "Weinstein Perelman Theory" because Eric Weinstein on Twitter has been pushing something similar with respect to Grisha Perelman turning down major math…
If you picked up The Poisoner's Handbook (amazon.com) looking for a fool-proof recipe, I hope you have read the book through and realized at the end that such a thing does not exist: you'll get busted. If they could figure it all out back in 1930s, can you imagine how much easier they can figure out a case of poisoning today, with modern sensitive techniques? And if you have read the book through, I hope you found it as fascinating as I did. Perhaps you should use your fascination with poisons to do good instead, perhaps become a forensic toxicologist?
My SciBling Deborah Blum (blog, Twitter…
The nearly complete skeleton of a Steller's sea cow (Hydrodamalis gigas) - it is missing bones from the wrist and hand. From Woodward, 1885.
It did not take long for the last remaining population of Steller's sea cow to be driven into extinction. Discovered by the German naturalist Georg Steller around the Bering Sea's Commander Islands in 1741, this enormous and peculiar sirenian became an easy target for Russian hunters. By 1768, it was gone. (The marine mammal would not be scientifically described until 1780, and today it is formally known as Hydrodamalis gigas.) Yet, despite the clear…
The "common cuttle-fish." From Mysteries of the Ocean.
About three decades before On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection would forever change biological science, the aspiring young naturalists Pierre-Stanislas Meyranx and Laurencet submitted a paper on mollusks to France's prestigious Academie des Sciences. For weeks they waited for a patron from within the scientific elite to recognize their work, but no response came. Ultimately they decided to take the more direct route of having the paper examined by a commission, and in 1830 the naturalists Pierre-Andre Latreille and…
The skull of Paranthropus boisei ("Zinj," "Dear Boy," "Nutcracker Man," etc.).
Louis Leakey had a problem.
During the summer of 1959 he and his wife Mary recovered the skull fragments of an early human scattered about the fossil deposits of Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania. The skull had been deposited among the shattered bones of fossil mammals and a collection stone tools, and this led Louis to conclude that it was one of our early ancestors. Only an ancestor of Homo sapiens could be a toolmaker, Louis thought, but the skull looked nothing like that of our species.
When Mary fit all the pieces…
Joanna Ebenstein of Morbid Anatomy has just unveiled a new website, the Secret Museum, to house her "exhibition of photographs exploring the poetics of hidden, untouched and curious collections from around the world." So if you can't make it to her show in NYC (through June 6), you can browse her virtual exhibition of photos - like the eerie fetal skeleton tableau above (from Paris, circa 17th century).