math
Time to preheat your ovens...the second annual Pi Day Pie Bakeoff wants your best creations to celebrate March 14. This year food mecca Serious Eats is our co-sponsor, meaning the prizes have gotten bigger and badder. The Grand Prize winner will receive $314 in warm, flaky cash—irrational change not included. You can also win a Simple as 3.141592 t-shirt from magazine mental_floss. Not bad for a few cups of flour and a sack of apples! But if you really want to win, it's time to get creative. Last year's champion Spicy Brittle Bacon Chocolate Pie (or Spicy Pi Bacon Squared) made the…
Boskone this past weekend was held at the Westin Waterfront in Boston, which has these funky double showerheads that they charmingly call the "Heavenly(R) Shower" (hype aside, they are very nice showers). The picture at right is courtesy of lannalee on Twitter, as I didn't bring a camera.
Why am I telling you this? Because there was a sign glued to the wall in the shower that read:
Refresh yourself, restore our world
One of your Heavenly(R) Shower heads has been turned off in an effort to minimize water usage and protect one of our most precious natural resources.
The smarmy enviroweenieness…
I've toyed around in the past with ways to use the Amazon sales rank tracker to estimate the sales numbers for How to Teach Physics to Your Dog. It's geeky fun, but not especially quantitative.
Yesterday, though, I found a reason to re-visit the topic: calibration data!
OK, "calibration data" is probably too strong a description. "Calibration anecdote" is more accurate.
Yesterday when I went into work a little after 10, a comment somebody made sent me to the actual Amazon page for the book, where I saw a little note next to the price information saying "Only 5 left (more are coming)-- order…
To most outsiders, modern mathematics is unknown territory. Its borders are protected by dense thickets of technical terms; its landscapes are a mass of indecipherable equations and incomprehensible concepts. Few realize that the world of modern mathematics is rich with vivid images and provocative ideas. -Ivars Peterson
Those of you who know me well know that I have little love for math for its own sake, but that I prize it as an incredible tool to help us understand and quantify physical systems. This has incredible applications, from figuring out what trajectory will succeed in a game of…
I forgot to include an option about this in the previous Dorky Poll, but this is one of the best ways I know to sort out righteous physicists from heathen mathematicians:
How do you like your angular coordinates?(polls)
Choose wisely.
Today's lecture in intro mechanics is a whirlwind survey of vectors. While I struggle to clear my head enough to be able to teach this stuff, here's a Dorky Poll to pass the time:
What's your favorite three-dimensional coordinate system?(survey)
This is a strictly classical subject, so please choose only one.
Over at Faraday's Cage, Cherish has a very nice post on Fourier series, following on an earlier post on Fourier transforms in the Transformers movie. She gives a nice definition of the process in the earlier post:
A Fourier Transform takes a signal and looks at the waves and then shows us the frequencies of all the waves. If we only have a single sine wave, like above, we will have a frequency that is zero everywhere except for the frequency of that sine wave. More complicated signals will be made up of several of these different frequencies and thus will have several peaks. The idea is that…
When I saw the data generated by the sales rank tracker Matthew Beckler was kind enough to put together, I joked that I hoped to someday need a logarithmic scale to display the sales rank history of How to Teach Physics to Your Dog. Thanks to links from Boing Boing, John Scalzi, and Kevin Drum, I got my wish:
For those not familiar with the concept, a log scale plots values on a scale that represents each order of magnitude as a fixed distance. So, the top horizontal line on that plot represents a sales rank of a million, the line below that a hundred thousand, the line below that ten…
I've been playing around with the spiffy sales rank tracker Matthew Beckler wrote, because I'm a great big dork, and enjoy playing with graphs. Here's a graph of the sales rank vs. time through 2pm EST today (plotted in Excel from the data table at the bottom of the page):
As I noted in my previous post on this, the downward-going jumps are striking, and probably indicate discrete book purchase events. There also seems to be a clear trend that jumps starting at higher numbers are larger than jumps starting at lower numbers. If we assume that's the case, what does that tell us about the…
One of the reasons I write here on ScienceBlogs is because of our associations with the New York Times, a journalistic news source that I'm proud of on most days.
Today is not one of those days.
It isn't just the Times, either, the BBC is busy botching this story, so is the Telegraph, the Daily Mail, and pretty much everyone else, except for TG Daily, which got it right.
If you go down to the bottom of Soudan Mine in Minnesota, you'll see an usual site for a mine: a group of giant physics experiments! Why? At the bottom of mineshafts, you have up to hundreds of feet of Earth protecting you…
The solar system is difficult to show correctly. Why? It is difficult because the size of things are vastly different. Let me use units common in solar-system astronomy, the Astronomical Unit (or AU). One AU is the distance from the Sun to the Earth. If I want to look at all the planets, I would need to go out to about 30 AU (to Neptune - remember that Pluto is not a planet). That is not a problem but then if I want to look at the size of even the Sun, it is just 0.001 AU across. And the Earth is even smaller, at 0.0001 AU. So that is the problem. The distance from the Sun to Neptune…
In the comments on one of my posts, someone pointed me towards Stephen Crothers, who gives the following argument (in a nutshell) as to why black holes cannot possibly exist:
General Relativity is our theory of gravity, which relates the curvature of space to the gravitational acceleration of objects.
This theory only works in certain regimes; it breaks down at the point of singularities.
A black hole, as predicted by Schwarzschild, is a singularity.
Therefore, since singularities are forbidden by General Relativity, there is no reason to think that black holes exist.
(You can watch his…
...we spend paltry sums for population planning, even though its spontaneous growth is an urgent threat to life on our planet.
There is no human circumstance more tragic than the persisting existence of a harmful condition for which a remedy is readily available. Family planning, to relate population to world resources, is possible, practical and necessary. Unlike plagues of the dark ages or contemporary diseases we do not yet understand, the modern plague of overpopulation is soluble by means we have discovered and with resources we possess.
What is lacking is not sufficient knowledge of the…
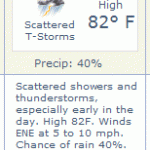
I have a bone to pick with The Weather Channel, and it has to do with misuse of statistics. This is something I noticed a long time ago, so it's about time I said something about it. The problem here is fairly obvious, so I'm sure many others have noticed this before. Also, this may not be specific to The Weather Channel, but I'm just using it as an example because that is where I have observed this problem.
To the left, you can see tomorrow's forecast for Austin, Texas, from The Weather Channel. The key piece of information here (for this post) is that there is a 40% chance of…
We're working on moving SteelyKid from formula to milk (which isn't going all that well-- dairy seems to make her gassy). This has led me to switch over to cereal in the mornings, since we're buying milk anyway, which frees up the time otherwise spent waiting for the toaster.
Cereal-wise, I tend to alternate between Cheerios (which we also buy for SteelyKid) and Raisin Bran-- my parents never bought sugary breakfast cereal, so I never developed a taste for any of those things. Being the ridiculous geek that I am, I've noticed something about the relative amounts of milk and cereal I use for…
I'm halfway through Graham Farmelo's Dirac biography at the moment, and enjoying it quite a bit. Farmelo cites Dirac as one of the first physicists to evaluate theories on their mathematical beauty, rather than waiting for experiments. This is in stark contrast to his Cambridge colleague Rutherford, who was highly skeptical of abstract theory, and preferred to deal in concrete experiments.
This is one of the great chicken-and-egg problems in science: Should data come before theory, or should theory come before data? Thus, this seems like a good topic for a poll:
How do you like your science…
Prompted by a discussion in another channel, a question for you all: What is your preferred type of calculator? That is, when you're doing some sort of problem involving math, and reach for a calculator, what do you reach for?
What Kind of Calculator Do You Use?(survey software)
I think I may have used this topic before, but not in a fancy radio-button poll.
Over in Twitter-land, Eric Weinstein is visiting the AMNH at the same time as a bunch of Orthodox Jews, and takes the opportunity for a little Q&A:
Me: Excuse me, but how is the phylogenetic tree reconciled with Torah.
Modern Orthodox Man: Lorentzian time dilation. It's a head hurter.
This is an interesting attempt to square the six-day creation story with modern science, and raises one obvious question: How fast must God have been moving for the six days of creation to last 13.7 billion years?
This is veering into Built on Facts territory, but the relevant formula is:
For six days (5.…
Dan Meyer, like most people, has long wondered whether there was a good way to predict which check-out line at the grocery store will be the fastest. Unlike most people, he used science to find an answer: "I spent ninety minutes last week just watching, counting, and timing groceries as they slid across a scanner." This produced a graph showing a roughly linear relationship between items in a cart and time spent checking out.
The conclusion: Each item adds 2.9 seconds on average, but each person adds 48 seconds on average. So you would rather be on line behind one person with a full cart than…
One of the odd things about the C-list celebrity life of a semi-pro blogger is that I get a bunch of requests to review books on physics-related topics. Some of these take the form of a book showing up out of the blue, others are preceded by a polite request from the author. Aaron Santos's How Many Licks? is one of the latter, which helps bump it up the list of things to do...
This is a short little book-- 176 pages total-- built around the idea of Fermi Problems, the order-of-magnitude estimates that Enrico Fermi was famous for. The idea is that, with a little basic knowledge and some really…