Science history
Here are some more unsung heroes of research: scanners (the human kind). In the 1950s, Donald Glaser invented the bubble chamber – a way to track infinitesimally small quantum particles as they winked in and out of existence. The idea – which may or may not have been tested in beer – was to create a large chamber of liquid under pressure next to a particle accelerator. As the beams hit their target, producing sprays of new types of short-lived particles, these energetic particles would leave tracks of bubbles in the liquid (usually hydrogen). Everything was caught on arrays of special high-…
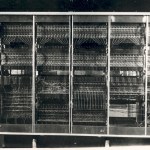
Google's official blog has a post today on the first computer in Israel: WEIZAC, built at the Weizmann Institute in the 1950s. Prof. Aviezri Frenkel gives a charming description of the project, including the fireworks when the machine was first turned on, in the presence of the VIPS who had come to see the new wonder.
http://googleblog.blogspot.co.il/2013/06/remembering-weizac-beginning-of.html
The foresight of the scientists who decided to build the computer is mentioned. But we can also thank them for their foresight in preserving this piece of computing history once newer computers…
We recently witnessed the disagreement over the official memorial for the 11 Israeli athletes killed at the Munich Olympics 40 years ago. Fewer remember the terrorist attack in the Lod airport a few months earlier – in May – in which 24 people lost their lives. One of those was the head of the Weizmann Institute’s Polymer’s Department, Prof. Aharon Katzir. (Somewhat ironically, in light of the later attack, Katzir had just returned from Germany, where he had co-organized a conference with Nobel laureate Manfred Eigen.)
Aharon Katzir
Aharon Katzir and his brother, Ephraim, who would later…
We don't mean to kvetch, but the new website we promised back in June is still as elusive as cold fusion. Scientific research, of course, is going strong, and we even continue to write about it, but no one can read about it on our website (and therefore, we can't offer links to articles on the newest findings).
In the meantime, here is the October image from our 2010-2011 calendar:
It looks like quite a simple apparatus, but in many ways, it was far ahead of its time. It was called a mechanochemical engine, and it was created at the Institute in the 1950s by Prof. Aharon Katzir. Katzir…
In 16th century France, there lived a king with a beautiful and somewhat mysterious mistress. Diane de Poitiers was almost 20 years older than Henri II but she looked like one of his contemporaries. She had skin of a near porcelain white and auburn hair as fine as silk thread.
Famed for her intellect as well as her beauty, Diane was not only the king's lover but one of his closest political advisors. He even encouraged her to sign some of his official correspondence HenriDiane. After Henri died in 1559, his angry and resentful widow banished Diane from the court. She died at the…
Last week, the U.S. Army announced that its excavation old chemical munitions dump - unfortunately located in one of Washington D.C.'s more elegant neighborhoods - had turned up remnants of two of the ugliest weapons developed in World War I.
By which I mean compounds used in the production of mustard gas and the arsenic-laced blistering agent Lewisite. In fact - this is my favorite part - the glassware used in Lewisite production started smoking as workers exposed it, halting the excavation for safety reasons.
The 1920s nickname for Lewisite, by the way, was "dew of death." But despite the…