sea level rise
On Class M, James Hrynyshyn shows us how climate change will benefit the economies of some U.S. counties while damaging many others. This mostly has to do with location; coastal areas and southern latitudes are more threatened, with Florida poised to suffer worst of all. James writes, "we're not just talking about polar bears anymore. It's now about jobs, wages, infrastructure, crime." Meanwhile, William M. Connolley reports Antarctica's Larsen C ice shelf is 12% smaller due to a giant iceberg splitting off and heading (presumably) toward Miami. Greg Laden says denial of global warming has…
About once a day, someone tells me that human caused climate change is not real because this or that thing in the latest report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) contradicts something I, or some other scientists or science writer, has said.
I've noticed an uptick in references to the IPCC report by those intent on denying the reality of climate change. This even happened at recent congressional hearings, where "expert witnesses" made similar claims.
How can that be? How can the flagship scientific report on climate change, the objective source of information about the…
The year 2016 was messy and expensive and full of climate change enhanced weather disasters. There were, according to Jeff Masters and Bob Henson, over 30 billion dollar disasters last year.
This is the fourth-largest number on record going back to 1990, said insurance broker Aon Benfield in their Annual Global Climate and Catastrophe Report issued January 17 (updated January 23 to include a 31st billion-dollar disaster, the Gatlinburg, Tennessee fire.) The average from 1990 - 2016 was 22 billion-dollar weather disasters; the highest number since 1990 was 41, in 2013.
The frequency of…
When the sea levels rose following the last major glaciation, most rapidly between around 18,000 and 10,000 years ago, somewhat less rapidly until about 6,000 years ago, a lot of interesting things happened.
I used to live, and do archaeology in, New England (the one in the US). It was always fun to contemplate George's Bank. George's Bank is a high place out in the ocean, not far from Boston. If you've ever been whale watching off P-town, you were probably out on George's Bank, where the baleen whales forage and frolic, and are easily found during the right season. This is also a great…
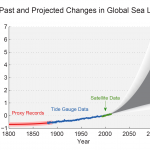
Sea levels are going to rise
The amount of carbon dioxide in the Earth’s atmosphere directly and indirectly determines the sea level. The more CO2 the higher the sea level. The details matter, the mechanism is complex, and as CO2 levels change, it takes an unknown amount of time for the sea level to catch up.
The present day level of CO2 is just over 400ppm (parts per million). For thousands of years prior to humans having a large effect on this number, the level of atmospheric CO2 was closer to 250. Human release of CO2 into the atmosphere by the burning of fossil fuel, and other human…
Human caused greenhouse gas pollution has locked us into a situation where the global sea level will rise, at an unknown rate, high enough to inundate most major coastal cities and vast areas of agricultural land in low lying countries, and wipe out thousands of islands. Entire countries (small, low lying ones, and pacific ocean nations) will either disappear entirely or be made very small. Even as we head towards a likely limit in global food production in relation to increasing demand, large productive agricultural areas will be destroyed. As far as I can tell, there is nothing to stop this…
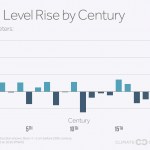
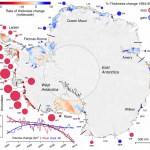
There is a new study by a French/English team looking at the rate at which Antarctic glaciers might contribute to sea level rise, due to global warming, between now and 2100 and 2200 AD.
The study produces several estimates, but suggests that glaciers in Antartica might contribute as much as 30 cm by 2100 and 72 cm by 2200. That is a large amount of sea level rise, but it is actually less than other studies that rely more on paleoclimate evidence have suggested. I personally have something of a bias towards paleo evidence; Good paleo evidence is evidence of what actually happened,…
A recent study that is getting a lot of press suggests that the massive ice sheets of Antarctica are on average growing rather than shrinking, and thus, not contributing to sea level rise. (The authors of the study warn that this will reverse in the near future with global warming.) However, there is reason to believe that these conclusions are incorrect.
Antarctica is the sleeping giant of climate change. Human activity, mainly the release of greenhouse gasses from burning fossil fuels, has been changing the climate rather dramatically for the last few decades, and the consequences of this…
I don't care that the director or CEO of an advocacy organization concerned with poverty is an active academic. Indeed, my view of active academics is that many are largely incompetent in areas of life other than their specialized field. If that. So really, if you told me there is this great advocacy organization out there run by a well established active academic I'd figure you had that wrong, or I'd worry a little about the organization. On the other hand, everyone should care that university positions be given to active academics with credentials. So, when the University of Western…
I did an interview with JD Goodwin at at Blue Streak Science. It is here. Great science podcast, check out their other items.
Here is the interview on iTunes.
What is not new
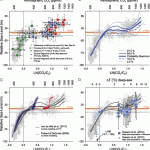
Ultimately sea levels will rise several feet, given the present levels of CO2 in the atmosphere. We already knew this by examining paleo data, and finding periods in the past with similar surface temperatures and/or similar atmospheric CO2 levels as today.
I put a graphic from a paper by Gavin Foster and Eelco Rohling at the top of the post. It does a good job of summarizing the paleo data.
If we keep pumping CO2 into the atmosphere at current, or even somewhat reduced, levels for a few more decades, the ultimate increase in sea levels will be significant. Find the 400–500…
A large portion of the glacial mass in Antarctic, previously thought to be relatively stable, is now understood to be destablizing. This is new research just out in Science. The abstract is pretty clear:
Growing evidence has demonstrated the importance of ice shelf buttressing on the inland grounded ice, especially if it is resting on bedrock below sea level. Much of the Southern Antarctic Peninsula satisfies this condition and also possesses a bed slope that deepens inland. Such ice sheet geometry is potentially unstable. We use satellite altimetry and gravity observations to show that a…
I recently noted that there are reasons to think that the effects of human caused climate change are coming on faster than previously expected. Since I wrote that (in late January) even more evidence has come along, so I thought it was time for an update.
First a bit of perspective. Scientists have known for a very long time that the proportion of greenhouse gasses in the Earth’s atmosphere controls (along with other factors) overall surface and upper ocean heat balance. In particular, is has been understood that the release of fossil Carbon (in coal and petroleum) as CO2 would likely warm…
Antarctica is pretty much covered with glaciers. Glaciers are dynamic entities that, unless they are in full melt, tend to grow near their thickest parts (that's why those are the thickest parts) and mush outwards towards the edges, where the liminal areas either melt (usually seasonally) in situ or drop off into the sea.
Antarctic's glaciers are surrounded by a number of floating ice shelves. The ice shelves are really the distal reaches of the moving glaciers floating over the ocean. This is one of the places, probably the place at present, where melting accelerated by human caused…
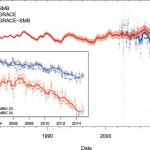
Human caused greenhouse gas pollution is heating the Earth and causing the planet’s polar ice caps and other glacial ice to melt. This, along with simply heating the ocean, has caused measurable sea level rise. Even more worrisome is this: the current elevated level of CO2 in the atmosphere was associated in the past with sea levels several meters higher than they are today. Even if we slow down Carbon pollution very quickly, we can expect sea levels to be at least 8 meters higher, eventually. How soon? Nobody knows, nobody can give you a time frame on this because the rate of melting of the…
Sea levels are rising with increasing global temperatures. It seems that whenever there is a new estimate of the rate of melting of one or more major parts of the polar ice caps, that estimate is higher than previously thought. By the end of the century, the most aggressive estimates suggest that we will have close to 2 meters (6 feet) of sea level rise along the coasts.
So,here are three sea level rise items for you.
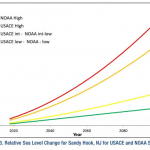
First, the Obama Administration will begin to plan for sea level rise in all major federal projects to which this variable pertains. See this item in the Washington Post.…
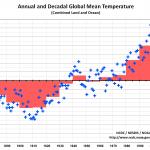
NOAA will announce today that 2014 was the warmest year during the instrumental record, which begins in 1880. The announcement, which addresses findings of both NOAA and NASA, will be made today at 11:00 Eastern. Below is the press release from NOAA.
I talked about this and other climate matters in a radio interview at Green Divas:
Michael Mann has made the following statements regarding this news:
2014 Was Earth’s Warmest Year On Record
Three major climate organizations (JMA, NASA, and NOAA) have now released their official estimates for the 2014 Global Mean Surface Temperature. Both JMA…
I just did an interview on Green Diva Radio, and talked about a lot of climate change science news. For those who want to see the sources, here is a quick summary:
On Friday, NASA and NOAA are expected to announce that 2014 was the hottest year on record. I had been planning to write an extensive blog post going into all sorts of details about how that works, how they calculate it, etc. But then the people at Climate Nexus wrote a post that would have blown mine out of the water with the detail and informtation provided in it. Go here to read this excellent post: 2014: Putting The Hottest…
Have a look at this new video from Peter Sinclair:
Peter has an interview with Jeff Goodell, contributing editor of Rolling Stone, which you will want to see. They talk about the political aspect of sea level rise in Florida.
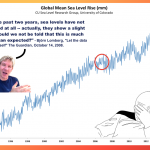
More about sea level rise here.
This is not a peer reviewed meta-study, but a meta-study nonetheless. Reuters has engaged in a major journalistic effort to examine sea level rise and has released the first part (two parts, actually). It is pretty good; I only found one paragraph to object to, and I'll ignore that right now.
There are two reasons this report is important. First, it documents something about sea level rise that I've been trying to impress on people all along. The effects of sea level rise do not end at one's perceived position of a new shoreline. Here's what I mean.
Suppose you are standing on a barrier…