biochemistry
Just as I was in the process of finishing my doctorate in August, I found out that my first first-author paper had been accepted for publication by The EMBO Journal. This was good news, because we were reporting some pretty fundamental findings in a relatively saturated field, and one of our competitors had managed to successfully stall the acceptance of this paper since March. Up until that point, witnessing this happen firsthand had been a somewhat frustrating and disillusioning experience for a young scientist, but I think that we were vindicated in the end. Anyway, this paper--and another…
The winners of this year's Nobel Prize in Chemistry have been announced, and the prize will be shared equally between Venkatraman Ramakrishnan, Thomas Steitz, and Ada Yonath "for studies of the structure and function of the ribosome." The information encoded in DNA is decoded to produce functional proteins in two stages: transcription (DNA --> RNA) and translation (RNA --> protein). This prize was awarded for the work that described this second stage in atomic detail, and you can read more about it in the scientific background document released with the prize announcement. This prize…
On Wednesday, the CDC reported that influenza A H1N1 viruses from 13 patients with confirmed diagnoses of swine flu had been tested for resistance to a variety of antiviral drugs. The good news was that all of the isolates were susceptible to the antiviral drugs oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and zanamivir (Relenza). However, all 13 were resistant to adamantane-based drugs (amantadine and rimantadine). Resistance to adamantane drugs (which were developed first) has actually become quite widespread among flu viruses in general, so oseltamivir and zanamivir are commonly the drugs of choice.
The…
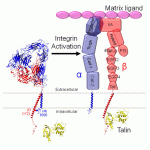
Cells in higher organisms exist in a dynamic environment, requiring the ability to alternately grasp and disengage from the three-dimensional web of their surroundings. One family of proteins in particular, the integrins, plays a key role in this process by acting as the hands of the cell. Spanning the cell membrane, they link the extracellular matrix to the cell's internal cytoskeleton. Integrins are especially interesting, though, because the cell uses them to uniquely pass signals in both directions across the membrane, and an integrin's adhesiveness for the extracellular matrix can be…
The grocery store magazine covers all say that home made gifts are big this year. So I thought, some of you might like to channel your inner Martha Stewart and make gifts with a science theme.
Reposted in honor of the holiday and the economy.
I'm here to help to you make a merry mug with one of our favorite molecules. Yep, we're talking caffeine.
1. First, we'll go to PubChem at the NCBI. It's not an exclusive (or even last) resort but there are lots of fancy molecules hanging around, just waiting to be discovered and put onto drinking containers.
2. Now, we'll look for a molecule. I'm…
Earlier today, the Nobel committee announced that the 2008 Nobel Prize in Chemistry has been awarded to Osamu Shimomura, Martin Chalfie, and Roger Y. Tsien "for the discovery and development of the green fluorescent protein, GFP." There's much to be said for how useful a tool GFP has been in cellular biology, but Alex Palazzo has already covered it at The Daily Transcript, so go check out his post for more.
Molecule of the Day has a post up about isotopically-enriched food that caught my eye for a couple of reasons. Firstly, the idea is wildly outrageous, and, secondly, this is something that actually gets joked about quite a bit in an NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) lab.
Any given element can come in various isotopes, which differ in the composition of their nuclei. The nuclei of different isotopes of the same element have the same number of protons, but they vary in their number of neutrons. Because the number of neutrons in a nucleus does not significantly affect the chemical properties…
The New York Times reported yesterday that "scientists find new receptor for HIV," referring to a paper published online in Nature Immunology on Sunday by Arthos et al. This is basically correct, although it would be more accurate to call the new receptor a co-receptor, since the infection of a cell with HIV still depends on the primary receptor, CD4, in combination with either CCR5 or CXCR4. The newly-identified co-receptor, just like the other HIV receptors, is a protein located on the surface of white blood cells (T-cells, specifically). HIV, like any other virus, can only replicate…
tags: Gerty Cori, 1947 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, glycogen metabolism, USPS commemorative stamps
A stamp featuring Biochemist Gerty Cori, who together with her husband won a Nobel Prize in 1947 for discovering how the body processes glycogen. Chemists found a small flaw in the drawing of the "cori ester" molecule, a derivative of glycogen discovered by Gerty, but the US Postal Service will issue the stamp anyway, in March.
Image: United States Postal Service [post box sized view].
An individual cell inside the human body is in a dynamic environment: it not only has to anchor itself to its surroundings but also be able to communicate with them and respond as appropriate. One group of proteins--the integrins--play a central role in all of these tasks. The integrins are large (about 200,000 Da) membrane-spanning proteins, and each integrin consists of two subunits (alpha and beta). The vast majority of the integrin is located on the exterior of the cell, where it anchors the cell to the extracellular matrix. Each subunit has a short tail inside of the cell, and the…
This is a fun puzzle. The pink molecule is a protein and the other molecule is a nucleic acid.
If I gave you the amino acid sequence of this protein, or the nucleotide sequence of this nucleic acid, what is the probability of finding a similar sequence in a different species (picked at random)?
A. High
B. Medium
C. Low
D. It depends on the database that you're searching.
You can have more than one answer.
Now, here's the hard part. Explain why you think your answer is correct.
This structure is called a "kissing loop" and I find that name just a bit odd, given the source of the structure.
Now, here's the puzzle: Why would I say that the name "kissing loop" is ironic?
The second paper from my undergraduate work at Texas A&M University was recently published in Molecular Cancer. The abstract can be found here, and the pdf of the full paper here. Molecular Cancer is an open access journal, so a subscription is not required to read the paper. It's also an online-only journal that publishes manuscripts immediately upon acceptance, so the version of the paper currently available is not the final (nicely-formatted) version. (Update: this now links to the final version of the paper.)
As with my first paper, which was published in October of this year, I'…
One of the goals of modern structural biology is to integrate the two traditionally distinct subfields of structural molecular biology (determination of the structures of macromolecules at atomic resolution) and structural cell biology (general architecture of of the cell and the localization of subcellular structures within it). The end result--as my research advisor at Oxford, Prof. Iain Campbell, often points out--is to be able to make a "molecular movie", at atomic resolution, of the whole cell. (Such a video might look something like this video from XVIVO and Harvard University--…
I think I can finally call myself a legitimate scientist (whatever that means), since last week one of the papers I worked on during my undergrad at Texas A&M University was published in The Journal of Cell Biology (JCB). I'm the fourth author on the paper, meaning that I was only peripherally involved (and made a much smaller contribution than the first author, Dr. Brian Saunders, and my advisor, Dr. George Davis, among others). Regardless, this is my first appearance in the peer-reviewed scientific literature, and since I (not surprisingly) find the subject of this paper incredibly…
After Monday's announcement of the 2006 Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology, followed yesterday by the announcement of the Prize in Physics, the Oscars of the sciences continue today with the awarding of the 2006 Nobel Prize in Chemistry to Roger Kornberg for his work on elucidating the molecular basis of transcription in eukaryotes. This decision is interesting for several reasons. First of all, Kornberg received the full Nobel Prize, not shared with any others, something that is fairly rare and further indicates the importance and breadth of the work he has done. Interestingly,…
The 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was announced this morning, with one half going to Andrew Fire and the other half to Craig Mello, both for the discovery of RNA interference (RNAi). The discovery of RNAi added a new layer to our understanding of how cells regulate gene expression and protect themselves from unwanted invaders, and, even more significantly, equipped biomedical scientists with a powerful new tool for studying protein function. Using RNAi, scientists are now able to dissect the genome of an organism, knocking down mRNA (and hopefully protein) expression, gene by…
From the archives:
(19 March 2006) Genetic engineering holds a great deal of promise, from potentially curing a variety of human ailments to addressing nutritional deficiencies through transgenic crops. One project even aims to engineer into bacteria the ability to generate a variety of alternative fuels. When it comes to genetic engineering and its emerging potential, it seems that the only real limit to the field is that it can only be used to design or improve something that is actually alive.
Despite this "limitation," some scientists have found that the raw material used in genetic…
There are a number of approaches scientists take to get at the fundamental nature of life, and one of those is elucidating the chemical structures of the molecules that make life happen, particularly proteins, which are the workhorses of the cell. One of the two primary methods for determining these structures is nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and the other is x-ray crystallography. My current work is in the former, meaning I spend a lot of time sitting in front of a huge magnet and even more time staring at a computer screen trying to make sense of the data I get from the magnet. As…
This is a plug for an event that the Oxford University Biochemical Society is putting together. This Monday, June 12th, at 4:00 pm the Oxford University Biochemical Society will be hosting a talk by Nobel Laureate Robert Huber in the University Museum (on Parks Road). The topic of the talk will be "Molecular machines for protein degradation", and more information on Huber and the 1988 Nobel Prize in Chemistry can be found here.