structural biology
"By night all cats are gray" - Miguel Cervantes in Don Quixote
I've always liked Siamese cats. Students do, too. "Why Siamese cats wear masks" is always a favorite story in genetics class. So, when I opened my January copy of The Science Teacher, I was thrilled to see an article on Siamese cat colors and proteins AND molecular genetics (1).
In the article, the authors (Todd and Kenyon) provide some background information on the enzymatic activity of tyrosinase and compare it to the catechol oxidase that causes fruit to brown, especially apples.…
Imagine a simple hike in a grassy part of South America. You hear a rattle and feel a quick stab of pain as fangs sink into your leg. Toxins in the snake venom travel through your blood vessels and penetrate your skin. If the snake is a South American rattlesnake, Crotalus terrific duressis, one of those toxins will be a phospholipase. Phospholipases attack cell and mitochondrial membranes destroying nerve and muscle function. Without quick treatment, a snakebite victim may be die or suffer permanent damage (1, 2).
The phospholipase from…
When finding a female scientists' data turns into an archeological treasure hunt.
A few months ago, I decided it would be interesting to celebrate various scientific contributions by making images of chemical / molecular structures in the Molecule World iPad app and posting them on Twitter (@MoleculeWorld). Whenever I can, I like to highlight scientific contributions from women on their birthdays. Tomorrow's post will feature Dr. Isabella Karle, an x-ray crystallographer who worked on the Manhattan project and solved structures of interesting molecules like…
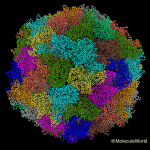
When my parents were young, summer made cities a scary place for young families. My mother tells me children were often sent away from their homes to relatives in the country, if possible, and swimming pools were definitely off limits. The disease they feared, poliomyelitis, and the havoc it wrecked were the stuff of nightmares. Children could wake up with a headache and end up a few hours later, in an iron lung, struggling to breathe.
Poliovirus colored by molecule in Molecule World.
…
Last year, I wrote about a scientific controversy over the structure of the influenza M2 proton channel, particularly over the protein's binding site for adamantane type anti-flu drugs. The Schnell/Chou model, based on solution NMR, had the drug binding to the outside of the channel, within the membrane (at a 4:1 drug:protein ratio). On the other hand, the Stouffer/DeGrado model had the drug binding inside the channel (1:1 ratio), based on X-ray crystallography studies.
A new study was recently published in Nature (the same journal that published the original two competing papers), based this…
When doing science, there's generally one totally optimal way of performing an experiment. But, there may also be several other less optimal means of gathering similar data, and one of those may be much more feasible than the totally optimal method. As a scientist, you have to determine whether this other method is sufficient, or whether it's necessary to expend the extra effort and/or resources on the more difficult method. Sometimes it's totally fine to take the simpler approach (and this will spare some of your precious time and your lab's precious funding), but this post is about a case…
Just as I was in the process of finishing my doctorate in August, I found out that my first first-author paper had been accepted for publication by The EMBO Journal. This was good news, because we were reporting some pretty fundamental findings in a relatively saturated field, and one of our competitors had managed to successfully stall the acceptance of this paper since March. Up until that point, witnessing this happen firsthand had been a somewhat frustrating and disillusioning experience for a young scientist, but I think that we were vindicated in the end. Anyway, this paper--and another…
Late last week, I received emails from two journals (The Journal of Biological Chemistry (JBC) and PLoS ONE) indicating that they are now incorporating interactive 3D images of molecular structures in their papers. The atomic coordinates of all published biomolecular structures have been available for some time at the Protein Data Bank. However, making sense of something as complex as a protein structure can require quite a bit of analysis. So, scientists go through great pains to represent important features of their structures in 2D images for publication. Ostensibly, this new functionality…
The winners of this year's Nobel Prize in Chemistry have been announced, and the prize will be shared equally between Venkatraman Ramakrishnan, Thomas Steitz, and Ada Yonath "for studies of the structure and function of the ribosome." The information encoded in DNA is decoded to produce functional proteins in two stages: transcription (DNA --> RNA) and translation (RNA --> protein). This prize was awarded for the work that described this second stage in atomic detail, and you can read more about it in the scientific background document released with the prize announcement. This prize…
On Wednesday, the CDC reported that influenza A H1N1 viruses from 13 patients with confirmed diagnoses of swine flu had been tested for resistance to a variety of antiviral drugs. The good news was that all of the isolates were susceptible to the antiviral drugs oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and zanamivir (Relenza). However, all 13 were resistant to adamantane-based drugs (amantadine and rimantadine). Resistance to adamantane drugs (which were developed first) has actually become quite widespread among flu viruses in general, so oseltamivir and zanamivir are commonly the drugs of choice.
The…
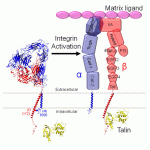
Cells in higher organisms exist in a dynamic environment, requiring the ability to alternately grasp and disengage from the three-dimensional web of their surroundings. One family of proteins in particular, the integrins, plays a key role in this process by acting as the hands of the cell. Spanning the cell membrane, they link the extracellular matrix to the cell's internal cytoskeleton. Integrins are especially interesting, though, because the cell uses them to uniquely pass signals in both directions across the membrane, and an integrin's adhesiveness for the extracellular matrix can be…
An individual cell inside the human body is in a dynamic environment: it not only has to anchor itself to its surroundings but also be able to communicate with them and respond as appropriate. One group of proteins--the integrins--play a central role in all of these tasks. The integrins are large (about 200,000 Da) membrane-spanning proteins, and each integrin consists of two subunits (alpha and beta). The vast majority of the integrin is located on the exterior of the cell, where it anchors the cell to the extracellular matrix. Each subunit has a short tail inside of the cell, and the…
One of the goals of modern structural biology is to integrate the two traditionally distinct subfields of structural molecular biology (determination of the structures of macromolecules at atomic resolution) and structural cell biology (general architecture of of the cell and the localization of subcellular structures within it). The end result--as my research advisor at Oxford, Prof. Iain Campbell, often points out--is to be able to make a "molecular movie", at atomic resolution, of the whole cell. (Such a video might look something like this video from XVIVO and Harvard University--…