diabetes
When blood sugar concentrations are elevated, humans run the risk of glucose binding to proteins in the blood and causing the irreversible formation of advanced glycation end products (AGE). Once formed, AGEs can bind to their receptor (RAGE) and stimulate inflammation and oxidative stress. This pathological signaling can be stopped by pieces of the RAGE protein that break off and form a soluble version called sRAGE. These soluble versions of RAGE are good because they can bind excess AGEs and prevent their effects.
A new study published in the American Journal of…
Image of cave dwelling Mexican tetra By Citron via Wikimedia Commons
Mexican tetra (Astyanax mexicanus) are a fascinating example of divergent evolution. Over time, some of these freshwater river fish washed into caves where they continue to live. With perpetual darkness, these cavefish have lost their ability to see along with their skin pigmentation. Oxygen and food are also hard to come by in the caves. In fact, the cave dwelling fish may go for months without eating as they wait for seasonal floods to deliver foods. Dr. Cliff Tabin (Harvard Medical School) recently presented his…
Photo of zebrafish housed at a research institute. By Karol Głąb CC BY-SA 3.0. via Wikimedia Commons
Who would have thought tiny fish could lead to big advances in medicine? Zebrafish (Danio rerio) and mammals have similar anatomy and physiology of the brain, eyes, gut, and cardiovascular systems. Some of the reasons why these fish are good models to understand cardiovascular physiology were recently explored in a new article published in Physiological Reviews.
Animal models are used in research that seeks to understand both normal physiological mechanisms as well as mechanisms…
Another day, another study that shows soda taxes work to reduce the consumption of beverages associated with costly chronic diseases in children and adults.
This time it’s a study on Mexico’s sugar-sweetened beverage tax, which went into effect at the start of 2014 and tacked on 1 peso per liter of sugary drink. Published this month in the journal Health Affairs, the study found that purchases of sugary drinks subject to the new tax went down more than 5 percent in 2014 and nearly 10 percent in 2015. At the same time, purchases of untaxed drinks went up by slightly more than 2 percent. The…
I know this is not a comparative physiology topic, but this article caught my attention as I know I just ate a rather high fat meal last week for Thanksgiving and I plan to do the same throughout the holiday season.
Insulin does more than just lowering blood sugar by increasing its uptake into tissues. It can also increase blood flow to the hippocampal region of the brain to help cognitive function. This area of the brain is important in memory formation and spatial orientation. A new study published in the American Journal of Physiology - Endocrinology and Metabolism used…
After years of alarming increases in child and adult obesity and billions spent to treat related medical problems, one might think health organizations and soda companies would be on firmly opposite sides of the fence. But a new study finds that a surprising number of health groups accept soda sponsorship dollars, inadvertently helping to polish the public image of companies that actively lobby against obesity prevention efforts.
“To be honest, it was really shocking,” study co-author Michael Siegel, a professor of community health sciences at Boston University School of Public Health, told…
The Michigan Physiological Society, a chapter of the American Physiological Society, held their 3rd annual meeting last week. As mentioned in a prior post, the keynote address was given by Comparative Physiologist Dr. Hannah Carey (University of Wisconsin School of Veterinary Medicine). You can read about her research in the prior post.
Here are other highlights from the meeting:
Seminars:
Photo of crayfish by "Krebse in Österreich", own work, CC BY 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=858592
...or as I prefer to view them:
Image of crayfish dinner By Игоревич (Own…
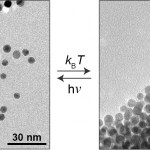
One day in the future, we may be treating our ailments with microbiotic combinations designed specifically to correct imbalances in our personal microbiomes. We’ll bring our prescriptions on rewritable paper and pay using shimmery optical chips embedded in our cell phone cases or maybe our jewelry. Or we’ll be waiting in our doctor’s office for a simple test of our microbiogenome to see if a light-based nanoparticle delivery treatment is working, while watching iridescent optical displays that change as we move...
These future scenarios (and many more) are all imaginary, but…
Image of baboon with offspring By RADION Imaginery / Kamil Wencel (RADION Imaginery / http://imaginery.radion.org/) [Attribution], via Wikimedia Commons
Malnutrition during pregnancy is a major global health issue that leads to restricted growth of developing fetuses making them more prone to death and disease. In fact, babies born from poorly nourished mothers are more likely to develop obesity, metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease as adults.
Researchers from the University of Colorado and University of Texas Health Sciences Center teamed up to examine whether the…
A common criticism aimed at those of us who are highly critical of various alternative medicine treatments and, in particular, of the "integration" of such treatments into conventional medical treatment is: What's the harm? What, they ask, is the harm of homeopathy, acupuncture, iridology, or traditional Chinese medicine? They argue that it's pretty much harmless, or, to quote Douglas Adam's The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy about earth, harmless. Of course, fans of the novels know that Ford Prefect, a contributor to the guide, reacting to Earthling Arthur Dent's outrage that the entry for…
Image of sheep from Wikimedia Commons
Insulin is a major hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar. Its main function is to lower sugar by increasing glucose uptake into muscle and fat cells. Insulin resistance is the hallmark of type 2 diabetes and occurs when tissues in the body are not able to respond to insulin resulting in sustained elevations in blood sugar, also known as hyperglycemia.
An alternative mechanism for lowering blood sugar is muscle contraction as it stimulates a pathway distinct from insulin in the muscles to cause glucose uptake from the blood. Exercise…
I was very impressed by the graduate and undergraduate students who presented their research at the Scholander poster competition sponsored by the Comparative and Evolutionary Physiology section of the American Physiological Society this afternoon. I am sure the winner of the competition will be very difficult to select.
Some highlights included:
Bridget Martinez, graduate student at the University of California - Merced whose research focused on hormonal changes that occur with fasting in elephant seal pups. In mammals, food deprivation leads to lower…
Sucrose
Molecules of sucrose tore apart in their bellies letting glucose course free in their veins.
Luckily for us, a system evolved long ago to capture that glucose and minimize it's potential for damage. Removing sugar from the blood and sequestering it in liver, fat, and muscle cells, minimizes the harm that might result if sugars were free to bind to proteins and our bodies were stressed by trying to flush excess glucose out of our system.
This holiday season, we give thanks for insulin and the biotech companies like Genentech that cloned the human gene and began to…
During the past year, not one state experienced a decrease in adult obesity rates and, in fact, six states are home to even higher rates than before, according to a new report released today.
This morning, Trust for America’s Health (TFAH) and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (RWJF) released “The State of Obesity: Better Policies for a Healthier America,” finding that adult obesity rates rose in Alaska, Delaware, Idaho, New Jersey, Tennessee and Wyoming. Mississippi and West Virginia tied to take the unenviable top spot, both with an adult obesity rate of 35.1 percent, while Colorado is…
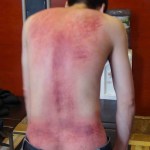
Image of electroacupuncture to the back from www.sandiegohealingarts.com
A new study published in AJP-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology suggests that electroacupuncture to the abdominal region may prevent increases in blood sugar concentrations after a meal by affecting insulin sensitivity and circulating free fatty acid concentrations. Granted this is not comparative physiology research, I find it interesting that electrical stimulation can have such a large impact on metabolism, in mice at least.
Drs. Nicola Abate and Jiande Chen, lead investigators…
I'm thinking it will be the food you eat that gets you. Here's why.
Humans eat a wide variety of foods; as a species, the diversity of species we eat is greater than any other animal by a very large margin, with the only quirky exception being the animals that we take along with us, the commensals such as rats and cockroaches. Most primates eat a high diversity of foods, but about two million years ago or a bit less, according to the “Cooking Hypothesis” (which a lot of people think is correct) we took an already diverse primate diet and added to it anything we might encounter in the…
Scientists use a 'gene gun' to insert a gene from a flowering plant called rockcress into the cells of wheat seeds. The genetically modified wheat became more resistant to a fungus called take-all, which in real life can cause "a 40-60% reduction in wheat yields."
T-cells from six HIV+ patients were removed from their bodies, treated with a zinc-finger nuclease designed to snip a gene out of the cell's DNA, and put back in the patients. Removal of the gene mimics a naturally occurring mutation which confers resistance to the HIV virus. But only 25% of the treated cells showed…
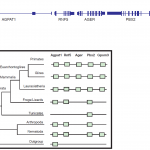
Figure 1 showing RAGE (aka: Ager) expression only in mammals from Sessa et al., PLOS ONE. 9(1): e86903, 2014.
RAGE stands for "receptor for advanced glycation end-products", also known as "AGER", and new research shows that it first appeared in mammals (Sessa et al., 2014). Despite the name, the receptor also binds other signaling molecules such as HMGB1, S100 proteins, beta-amyloid, phosphatidylserine, among others (Xie et al., 2013). RAGE is reportedly involved in diabetes, cardiovascular disease, atherosclerosis, osteoarthritis, cancer, Alzheimer's disease, as well as liver and renal…
Image of a grizzly bear at Yellowstone National Park from http://free-naturewallpaper.com/nature-images/animals/bears/Grizzly-at-…
I was so excited to see a story featuring grizzly bears (Ursus arctos horribilis) in the Wall Street Journal yesterday. The article was about how Dr. Kevin Corbit at Amgen Inc. is studying grizzly bears in the Bear Center at Washington State University to learn more about obesity. The 12 animals living in the facility were either rescued from places where they were captured after getting too close to humans or were born at the facility. Dr. Corbit was quoted in…
A new study from Science Translational Medicine (DOI:10.1126/scitranslmed.3006534) presents data showing that tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA), a compound isolated from the bile of bears, may actually slow the development of type 1 diabetes (in mice at least). It is thought to work by reducing stress responses from the endoplasmic reticulum in the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas which become defective in type 1 diabetes. Use of bear bile is common in traditional Chinese medicine, and at one time led to near-extinction of black bears in China. Fortunately, synthetic versions of…